What Are AI Agents? Everything Beginners Should Know
Multi-Agent Systems | AI vs Automation | Blockchain App Development
Curious to know about what are AI agents and how they work? Welcome to our AI agents guide, created to help beginners and business leaders unravel the latest advancements in autonomous digital agents revolutionizing the way businesses and individuals tackle tasks.
These intelligent digital collaborators autonomously make decisions, learn from real-time data, and act proactively to achieve goals. Unlike traditional tools that require explicit instructions, AI agents adapt across various domains, continuously improving with minimal human intervention. They boost productivity, reduce costs, and enhance accuracy around the clock, transforming everything from fraud detection in banking to personalized customer experiences.
In this guide, you’ll learn what AI agents are, how they differ from other artificial intelligence tools, their key components, practical applications across industries, benefits, challenges, and what to expect in the future.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are advanced software programs that perform tasks autonomously to achieve specific goals. They make decisions based on predefined objectives and real-time data. These agents rely on AI frameworks such as machine learning (ML) models and natural language processing (NLP) to properly understand and handle diverse inputs, responding accordingly. Unlike traditional programs, which depend on humans to carry out predefined tasks, AI bots can interpret their environment. They make choices based on available data and act proactively rather than simply reacting to user instructions.
Key features of an AI agent system include:
- They can work independently without needing much help from people.
- They keep improving their performance by using machine learning algorithms and AI in software development.
- They understand and communicate like humans do.
- They quickly analyze information and respond immediately.
- They can handle and adapt to multiple tasks across different domains.
- They work smoothly with humans and ask for help when things get tricky.
In banking, AI agents help improve customer service and security. They handle common questions anytime, like checking account info or resetting passwords. They also monitor transactions to spot possible fraud and alert humans when needed. This saves time, cuts costs, and protects customers. AI agents can even assist loan officers by quickly reviewing financial documents, speeding up decisions. Overall, AI agent development in financial services focuses on creating the best AI agents designed for precision and compliance.
How AI Agents Differ From Other AI Tools
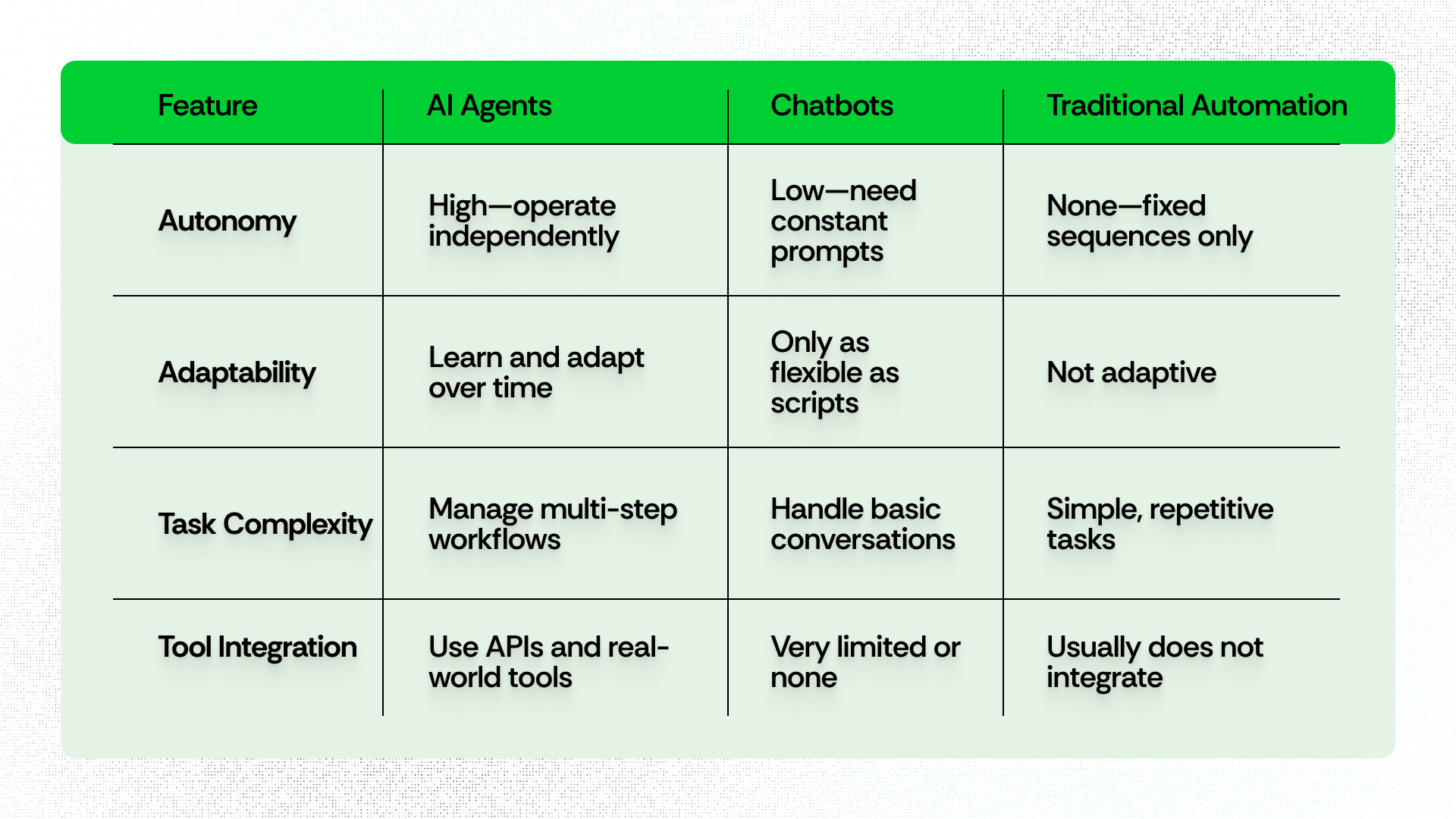
AI agents represent an advancement over familiar AI tools like chatbots and automation scripts:
When comparing AI agents vs chatbots, it becomes clear that while chatbots and scripts are like appliances that perform one task on request, AI agents are like skilled assistants, capable of context-switching, prioritizing, and initiating new actions as situations evolve.
An intelligent agent in AI can analyze complex scenarios and autonomously make decisions, often combining abilities seen in both agentic AI vs generative AI: agentic AI focuses on purposeful autonomous decision-making, while generative AI emphasizes content creation and response.
Core Components of AI Agents:
There are many kinds of AI agents with different capabilities, and their behavior depends on the agentic architecture they operate within. However, despite this variety, these agents share key components that are essential for building adaptive and intelligent systems. Let’s explore each of these components below.
- The Brain (Reasoning Engine): This usually involves large language models (LLMs) or similar advanced models, enabling nuanced understanding, planning, and decision-making.
- Memory: Agents store information about past tasks, user preferences, and outcomes. This memory can be short-term (during a session) or long-term (across weeks and months), allowing more personalized and contextual behavior.
- Knowledge Base: Some agents tap into live data feeds, company databases, documentation, or even the internet to bring relevant knowledge to every task.
- Tools and APIs: To accomplish objectives, agents need to act—placing orders, sending emails, updating calendars, or controlling physical devices via APIs, applications, or robotic components.
- Prompting/Instruction System: Complex instructions are broken down by the agent, which identifies the necessary steps, sequences, and fallback plans autonomously.
- Sensors and Actuators: In robotics or an Internet of Things (IoT) platform, agents gather data from their environment (temperature, photos, audio) and manipulate it using actuators (motors, switches).
Benefits of AI Agents
AI agents have become a big help for all kinds of businesses because they make work easier and faster. These smart programs take care of tasks that used to take a lot of time or were prone to mistakes, freeing up teams to focus on what really matters.
Have a glance at AI agents benefits and how they are making a real difference:
- Boosting Productivity: AI agents handle boring, repetitive jobs like data entry or scheduling, so people can spend their time on bigger, more important projects. They keep things running smoothly by automating processes without needing a lot of oversight.
- Improving Accuracy: These agents are great at spotting errors and catching details humans might miss. Whether it’s crunching numbers, checking facts, or reviewing data, AI agents deliver dependable results that save time and avoid costly mistakes.
- Working 24/7: Unlike humans, AI agents don’t need breaks or sleep. They can provide support and manage tasks all day and night, which means businesses never miss a beat when it comes to customer service or backend work, even outside regular office hours.
- Cutting Costs: Since AI agents can do in minutes what might take humans hours, companies save money on labor and reduce errors that might lead to extra expenses. This makes budgets stretch further without sacrificing quality.
- Growing with Your Business: As your business grows, AI agents can easily adjust to handle more work or new challenges. This flexibility helps companies stay efficient and keep up with demand, no matter how fast they expand. Simply put, leveraging artificial intelligence business through AI agents enhances scalability, customer experiences, and operational excellence.
In summary, AI agents not only automate tasks and improve productivity but also elevate decision-making, customer experience, scalability, security, and adaptability, making them transformative tools for businesses in 2025.
How do AI Agents Work?
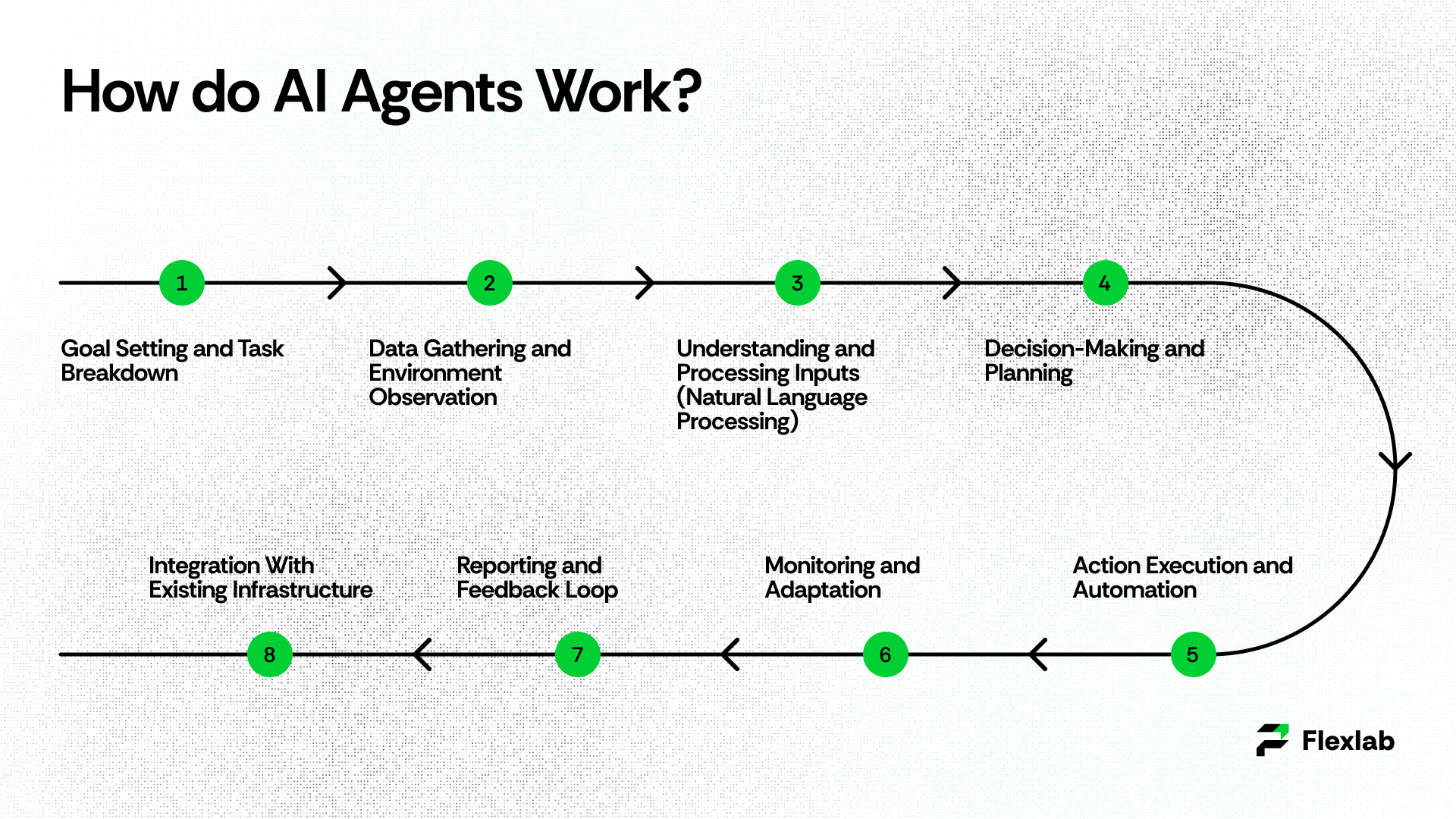
Below is a typical, detailed workflow that shows how modern AI agents operate from start to finish:
1. Goal Setting and Task Breakdown
AI agents work by autonomously performing complex tasks through a series of coordinated steps powered by advanced technologies like large language models (LLMs), machine learning, and natural language processing. The workflow begins when a clear goal or instruction is set, such as “handle customer support” or “manage inventory.” The agent analyzes this goal and breaks it down into smaller, manageable subtasks.
For example, it might categorize requests, retrieve relevant data, or perform specific actions. This breakdown allows the agent to prioritize tasks and plan a logical sequence of operations to efficiently achieve the overall objective.
2. Data Gathering and Environment Observation
Next, the agent collects the necessary data inputs from various sources, including databases, APIs, user inputs, sensors (in case of physical agents), or real-time systems. AI agents continuously observe their environment to understand context and any changes, which is vital for adapting decisions and actions. This step often involves data integration techniques to pull in both structured and unstructured data needed for processing.
3. Decision-Making and Planning
Once the inputs are processed, AI agents apply decision-making algorithms and reasoning engines—often powered by large language models, reinforcement learning, or rule-based systems—to evaluate the gathered data. The agent determines the best course of action for each subtask and plans multi-step workflows. Sometimes it includes fallback or alternative strategies if obstacles arise. For complex tasks, the agent prioritizes, sequences, and may loop back on subtasks based on interim results and user or system feedback.
4. Action Execution and Automation
After planning, the AI agent automates task execution. This can involve Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools to perform rule-based repetitive tasks like data entry or report generation, function calls and APIs to interact with software systems, databases, or external tools, and—for agents tied to physical systems—using actuators or sensors to manipulate hardware or environments. Actions such as sending emails, updating records, triggering workflows, or controlling devices are performed autonomously or semi-autonomously as required.
5. Monitoring and Adaptation
Throughout the process, the AI agent monitors outcomes and system feedback to ensure that objectives are being met. These agents learn from both successes and failures, using machine learning to improve future decisions and adapt to changing data. When tasks are too complex or need human judgment, the AI agent escalates them to a person or a more advanced system, ensuring smooth collaboration between AI and humans.
6. Reporting and Feedback Loop
Upon completing tasks, AI agents generate performance reports and summaries, providing transparent insights into actions taken and results achieved. This documentation supports auditing, compliance, and continuous improvement efforts. Feedback from users or operational data then feeds back into the system to refine models, update workflows, and enhance the agent’s capabilities over time.
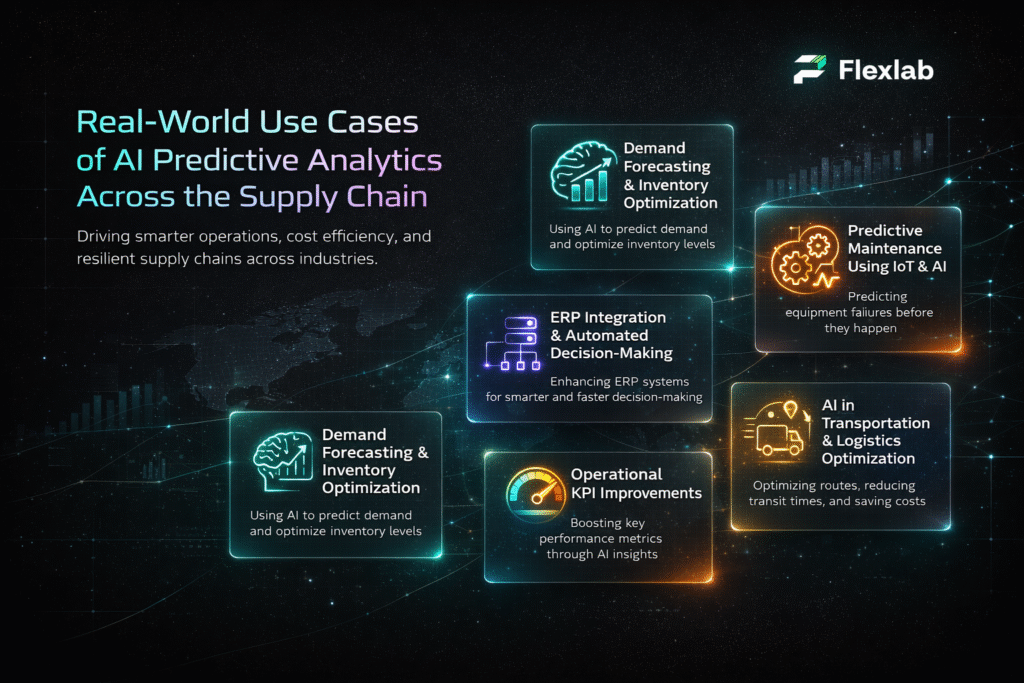
Real-World Use Cases of AI Agents (2025)
Different types of AI agents are making a big difference in many industries. They take care of tasks, save time, and help work get done better. Let’s check out some examples of how AI agents are being used in different fields.
AI Agents in Finance
AI agents in finance are streamlining operations and enhancing customer experience. For example, Bank of America’s Erica has surpassed 2 billion interactions, helping over 42 million customers with balance inquiries, bill payments, and spending tracking. Financial institutions now use virtual agents for fraud detection, customer service automation, and document processing, leading to higher accuracy and operational cost reductions. Automated invoice handling and expense management with AI agents have been shown to cut processing costs by up to 70% and boost accuracy beyond 90%.
AI Agents in Healthcare
In healthcare, AI agents are increasingly assisting with diagnostics, administrative automation, and patient support. For example, Babylon Health uses an AI assistant to instantly analyze symptoms and provide guidance, easing the burden on staff and speeding up care. Moreover, advanced systems like Massachusetts General Hospital’s AI diagnose conditions with over 90% accuracy, detecting lung nodules at 94% versus 65% for radiologists. As a result, AI-driven automation and digital health assistants could save the U.S. healthcare system up to $150 billion annually.
AI Agents in Retail
Retail businesses, for instance, leverage AI agents to provide personalized customer experiences and streamline operations. For example, Amazon’s Rufus is a conversational AI tool that helps identify suitable products and make personalized recommendations. Studies show that conversational agents in retail can lead to a 12% increase in customer satisfaction and reduce purchase abandonment by almost half. AI agents also optimize inventory and customer support, ensuring 24/7 service without overloading staff.
AI Agents in Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies use smart AI assistants for real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and process automation. Siemens’ AI-powered assistants assist engineers by generating code and diagnosing machine faults, reducing manual effort. Predictive maintenance agents can lower unplanned downtime and save up to 14% on costs. Meanwhile, AI-enabled quality control delivers up to 99.9% defect detection accuracy, leading to greater efficiency and fewer costly errors.
Limitations and Challenges
AI agents hold significant promise; however, they also come with notable limitations and challenges. One major issue is reliability. Even the most advanced AI agents can misunderstand rare or unusual cases or behave unpredictably in new situations. Therefore, regular monitoring and fallback plans are essential. In addition, privacy and security represent another critical challenge. Since these agents often require access to sensitive data to perform effectively, this demand calls for strong encryption, authentication, and strict compliance with regulations.
Human oversight is also necessary, especially for high-stakes decisions such as financial approvals, legal advice, or healthcare interventions. In these cases, human review or intervention ensures safety and correctness. Finally, intelligent digital agents must continuously adapt. Outdated rules, stale data, or evolving business requirements can degrade their performance over time. This makes ongoing review and retraining essential to maintain effectiveness. Moreover, this awareness of the risks of AI agents guides the work of any serious AI agent development company and reflects industry best practices for safer deployment.
What Can We Expect in the Future?
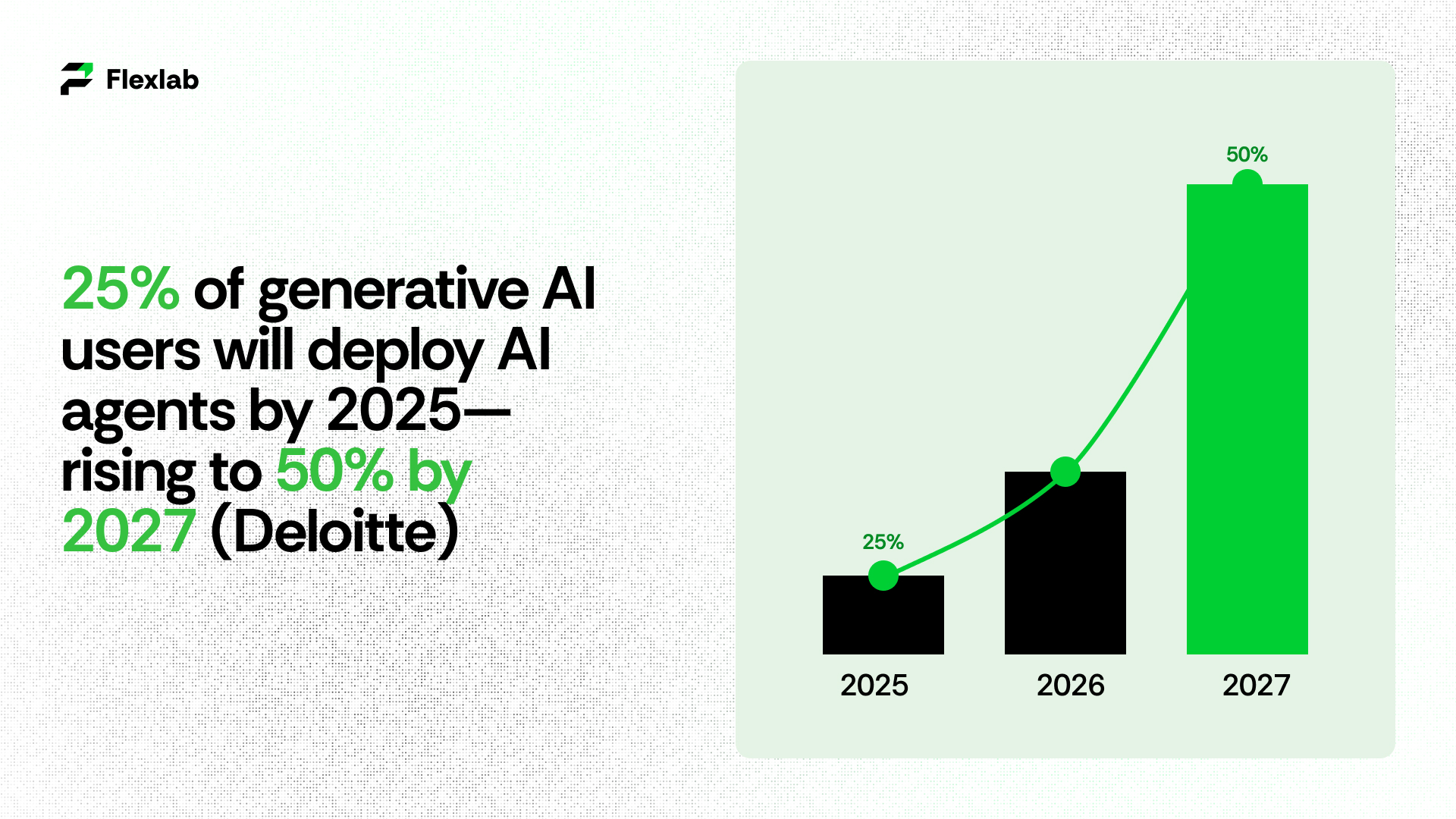
Many organizations are gearing up to adopt AI agents. According to a Capgemini report, about 82% of companies plan to implement AI agents by 2026. Deloitte also predicts that 25% of enterprises using generative AI agents will deploy AI agents by 2025, and this number is expected to grow to 50% by 2027. These AI agents won’t just be for general use; they will play bigger roles in specialized fields like finance, retail, and healthcare.
Looking ahead, AI-powered agents are evolving in some exciting ways. Instead of just responding when asked, they’ll start anticipating needs and solving problems proactively. They’ll offer more personalized experiences by learning your habits and preferences. For example, they might recommend products based on what you browse or provide tailored health advice. Emotional intelligence will improve too, meaning they can recognize when someone might be upset or stressed. They will respond with empathy, which could make a big difference in mental health support.
Smart digital helpers will get better at communicating by using a mix of text, voice, images, and video. As a result, interactions will feel more natural and effective. Furthermore, with deeper connections to smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), these agents will help automate daily tasks in smart homes, offices, and even entire cities. For instance, they can manage your shopping list and handle travel plans automatically.
At the same time, there’s a strong focus on making AI responsible and ethical. Developers and companies are working to reduce biases and promote fairness. They also aim to ensure AI systems are trustworthy and inclusive. This ethical approach is essential for widespread acceptance and beneficial integration of AI in society.
Overall, AI agents are set to become smarter, more intuitive partners in both work and everyday life. They will transform how we interact with technology, making many tasks easier and more efficient.
Unlock Seamless Automation and Growth with Flexlab AI Agents
At Flexlab, we offer comprehensive AI agent development services. We also specialize in developing artificial intelligence AI solutions powered by cutting-edge AI and blockchain technologies that transform how businesses operate and grow. By seamlessly integrating advanced automation, secure blockchain platforms, and an intelligent agent in AI systems, we help organizations optimize workflows, enhance decision-making, and deliver personalized, real-time experiences that drive efficiency and innovation.
Our expert team ensures your digital solutions not only perform flawlessly across web and mobile but also remain secure, scalable, and continuously optimized through proactive maintenance and upgrades. We provide tools, including AI agent builders platform and access to robust AI agent marketplaces, to empower businesses
Partnering with Flexlab means unlocking the full potential of AI agents to revolutionize your operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead in today’s fast-evolving digital landscape. Contact us today or explore our portfolio to see how we can help drive your business forward.
Ready to Grow Your Business?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email us: info@flexlab.io
Discover More:
- What are Multi-Agent Systems: Guide to Enterprise Automation
- AI vs Automation: Decoding the Differences for Business Success
- Blockchain App Development: The Complete Guide for Businesses
How to build an AI agent in 2025?
To build an AI agent in 2025, start by clearly defining your agent’s purpose and primary goals. Next, collect and prepare high-quality, task-specific data to ensure effective training. After setting up, proceed to train, test, and refine your agent to meet the desired performance benchmarks. Finally, deploy your AI agent, continuously monitor its performance, and regularly update it to improve accuracy and ensure it stays aligned with evolving business needs.
Who are the Big 4 AI agents?
The Big 4 AI agents in 2025 are OpenAI’s Operator, Devin AI by Cognition Labs, Claude by Anthropic, and Amazon’s Nova Act. These leading virtual agents offer advanced automation, adaptability, and multi-step task handling, powering intelligent workflows and autonomous decision-making for enterprises.
Can I build AI agents without coding?
Yes, you can build AI co-workers without coding in 2025, thanks to powerful no-code platforms. These tools offer drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-built templates, and easy integrations with popular apps like CRMs and messaging platforms. You can also test and deploy agents that handle complex tasks without writing code.

























7 Responses
Informative post! I was actually searching for
a tutorial on how to get access to OurDream AI VIP features.
Appreciate it for sharing this valuable information.
This guide really helped me to understand OurDream AI without issues.
I’ll certainly share this page for future reference.
Continue posting helpful stuff!