The Role of Multi-Agent Systems in Modern Enterprise Automation
Blockchain Development | AI Development Company | Blockchain App Development
Multi-Agent Systems are changing the game in enterprise automation – are you ready to see how they can help your business work smarter and faster? These systems use multiple intelligent software agents that work independently yet coordinate perfectly, acting like a team to handle complex tasks that single AI agents can’t manage alone. From improving supply chain efficiency to automating IT operations and enhancing customer service, multi-agent systems offer scalable, flexible solutions that help businesses stay ahead in today’s fast-paced world.
In this blog, we’ll explore what multi-agent systems are, how they function, their advantages over single AI agents, real-world examples, and how your company can start leveraging this powerful technology today.
What are Multi-Agent Systems?
A multi-agent system (MAS) is a network of smart software agents that operate, communicate, and make decisions independently. Think of these agents as digital teammates—each able to analyze what’s happening around them, and as a result, take action on their own and work together to solve bigger challenges.
Here’s what sets multi-agent systems apart:
- Defined Roles: Each agent is programmed to do specific tasks or manage certain parts of a business process. For example, one agent might track inventory, while another manages customer service requests.
- Independent Decision-Making: Agents don’t need someone hovering over them. Instead, they’re designed to think for themselves—analyzing data, spotting issues, and deciding on next steps based on pre-set logic.
- Team Communication: Just like co-workers, these agents share information with other software. This allows them to coordinate tasks, avoid conflicts, or even negotiate the best way to get things done.
- Shared Goals: Although each agent has its specialty, they’re all working toward the organization’s bigger objectives—whether that’s cutting costs, speeding up delivery, or improving customer experience.
According to a Gartner forecast cited by Talan, 75% of large enterprises are expected to adopt multi-agent AI systems by 2026, highlighting their growing importance in enterprise AI.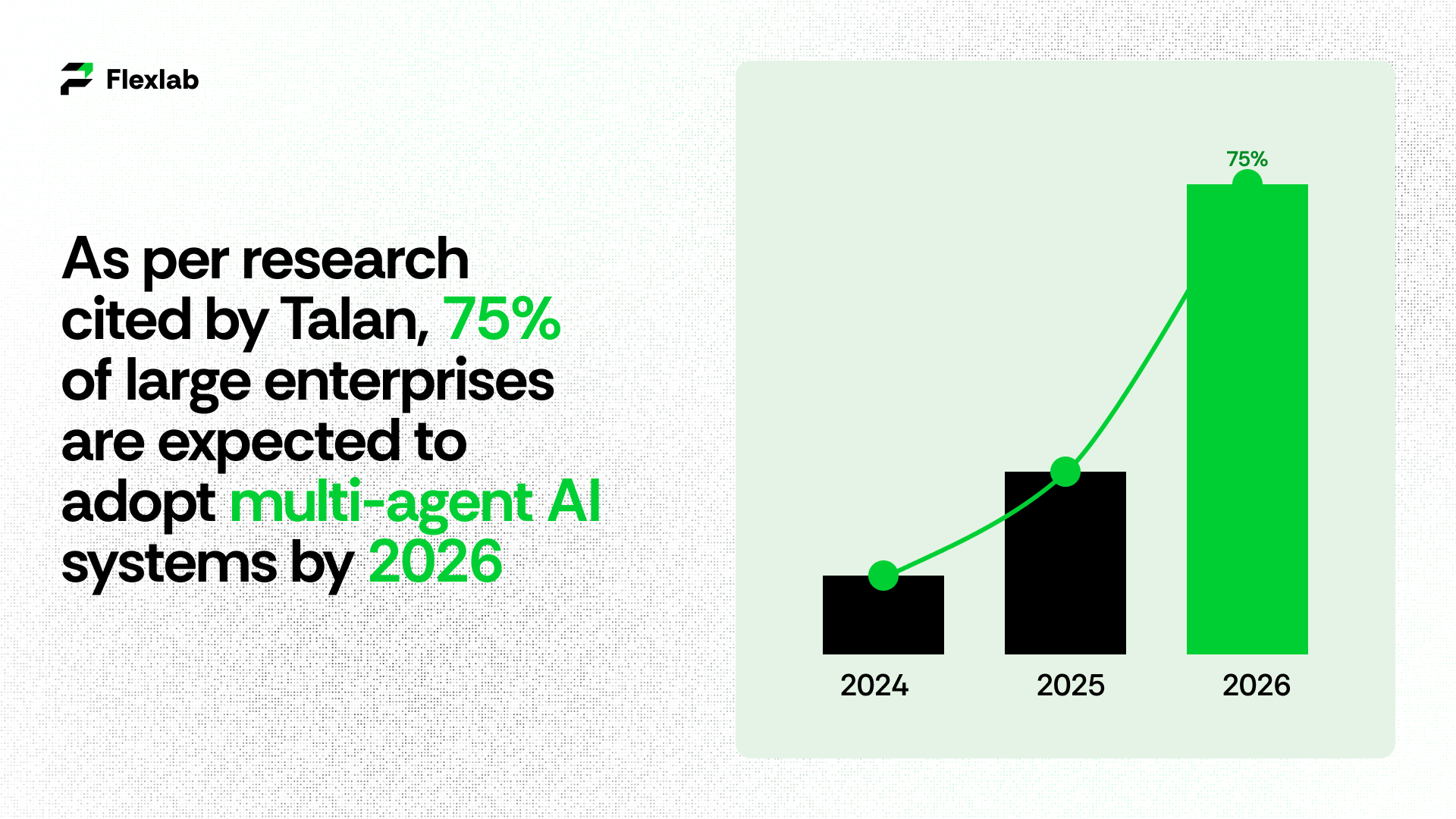
In short, multi-agent systems act like an all-star digital team, handling different jobs independently but always working toward your company’s success. This makes them especially powerful for businesses looking for smarter, more scalable automation.
How Do Multi-Agent Systems Work?
Multi-agent systems operate by having multiple intelligent software agents, each with its own unique abilities and responsibilities, that work both independently and together to accomplish larger goals. Each agent is designed to sense its environment, make decisions based on available information, and act quickly on those choices. What makes multi-agent systems especially effective is the way these agents actively communicate and share information. This ongoing exchange allows them to coordinate their actions, handle tasks more efficiently, and respond quickly to changes or challenges.
Depending on the setup, there may be a central coordinator agent guiding the process. Alternatively, the system might be fully decentralized, allowing all agents to make decisions collectively. For example, in a modern warehouse, separate agents might control different robots or processes. Together, they coordinate inventory movement and shipping schedules seamlessly. By enabling agents to support each other and step in when something goes wrong, multi-agent systems deliver solutions that are more robust, adaptable, and efficient than traditional single-agent approaches.
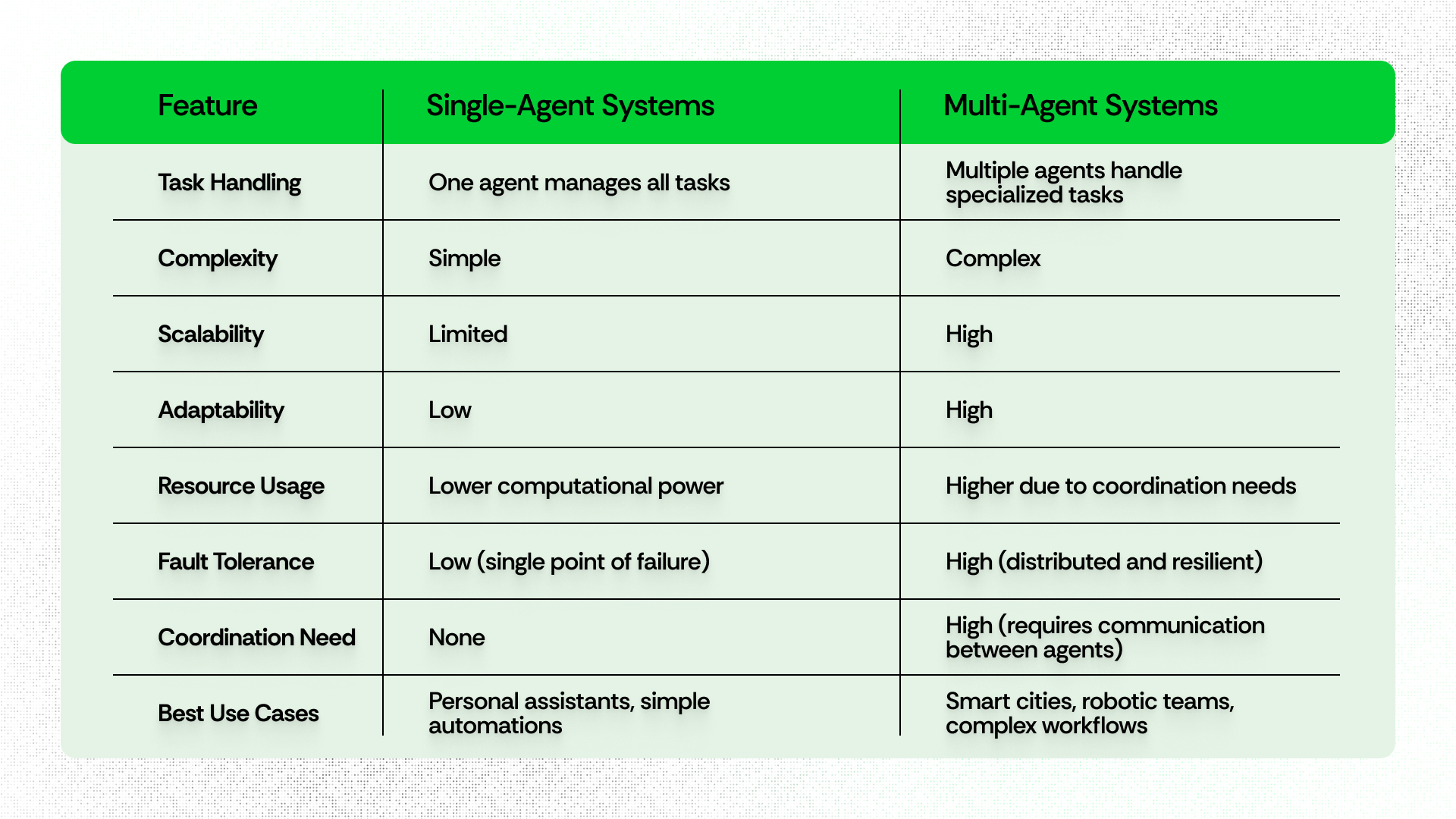
Difference Between Multi-Agent Systems and Single AI Agents
A single AI agent is designed to handle all tasks by itself. It operates independently, making decisions without collaborating with others. This approach is simple and efficient for straightforward, well-defined problems, like a personal scheduler or a spam filter. Because it focuses on one task or domain, it uses less computing power and is easier to design, test, and maintain. However, single-agent systems can struggle with complex, rapidly changing environments or tasks that require diverse skills.
On the other hand, multi-agent systems (MAS) consist of multiple specialized AI agents working together. Each agent has a unique role and handles a specific part of the overall task. These agents communicate and coordinate with each other, sharing information and dividing work to tackle complex, dynamic problems more effectively. For example, in smart traffic management, different agents might control traffic signals, monitor congestion, and reroute vehicles—all collaborating to optimize city-wide traffic flow. While MAS are more powerful and adaptable, they require greater computational resources, careful coordination, and more complex design to avoid overlaps or communication errors.
In summary, single-agent AI is great for simple, isolated tasks, while multi-agent systems excel in scenarios needing teamwork, flexibility, and scalability.
Examples of Multi-Agent Systems Across Industries
Multi-agent systems (MAS) are reshaping how organizations automate complex operations by coordinating multiple intelligent agents that work together. Here are some in-depth examples across key industries showing the power and versatility of MAS.
Clinical Trial Recruitment and Patient Care Coordination
In the pharmaceutical and healthcare sector, MAS brings revolutionary improvements to clinical trial recruitment, a traditionally slow and costly process. Agents representing patients, physicians, and trial coordinators automatically scan electronic health records (EHRs), demographic data, and eligibility criteria to identify potential participants quickly. This automation reduces manual screening by around 40%, accelerates enrollment, and improves trial success rates.
Moreover, MAS enables distributed diagnostic reasoning, where specialist agents collaborate on complex diagnoses by sharing lab results, imaging data, and genomic profiles. In practice, a multi-agent system acts like a virtual care team—agents assigned to physicians, labs, pharmacies, and equipment communicate in real time to coordinate treatments, monitor patient outcomes, and update care plans dynamically.
For example, the ClinicalAgent multi-agent system integrates advanced large language models with multi-agent frameworks to predict clinical trial outcomes and estimate trial durations, improving
predictive accuracy and operational efficiency. This intelligent collaboration ensures adaptive, personalized treatments and optimizes hospital workflows by simulating “what-if” scenarios to reduce bottlenecks and improve patient safety.
Financial Portfolio and Risk Management
Financial services harness MAS to deliver smarter portfolio optimization and risk management. Instead of relying on a single monolithic system, diverse agents specialize in tasks like market analysis, fraud detection, compliance monitoring, and client risk profiling. These agents autonomously analyze real-time market data, detect suspicious behaviors for AI fraud detection, and recommend investment adjustments.
MAS enables dynamic portfolio diversification by combining strategies—such as value investing and momentum trading—where agents continuously negotiate and rebalance investments based on market fluctuations and client preferences. This decentralized network improves responsiveness and reduces the risk of cascading failures common in centralized finance systems. Additionally, MAS automates compliance reporting, helping firms maintain transparency and meet strict regulations efficiently.
Adaptive Supply Chain Optimization and Logistics
Supply chains are dishonorably complex, impacted by unpredictable factors like weather, traffic, and supplier constraints. Multi-agent systems excel here by allowing each supplier, warehouse, and shipping agent to monitor local conditions and coordinate with others in real time to adapt plans dynamically.
For instance, when a delivery route is blocked due to a traffic jam or strike, agents reroute shipments autonomously, minimizing delays and waste. Forecasting agents collaborate to adjust inventory levels based on demand signals, reducing overstocking or stockouts. This orchestration relies on workflow automation software, AI reasoning, and autonomous decision-making AI to synchronize thousands of supply chain touchpoints instantly. Such MAS-driven supply chain optimization has been shown to improve on-time delivery rates and reduce operational costs significantly.
Autonomous Vehicles and Smart Traffic Systems
Multi-agent AI is at the core of developing safer, more efficient autonomous vehicle networks and smart infrastructure. Agents control individual vehicles, traffic lights, and road sensors, continuously exchanging data to optimize traffic flow, avoid collisions, and reduce congestion.
Agentic AI systems utilize reinforcement learning, enabling vehicles and infrastructure to develop optimal coordination strategies through experience. Furthermore, integration with large language models helps agents interpret natural language commands and complex sensor inputs, advancing user interaction and autonomous functions. These systems also support cybersecurity efforts by detecting anomalies and coordinating responses against potential threats.
Energy Management and Decentralized Trading
In energy grids, MAS manages distributed resources such as solar panels, wind farms, and energy storage units. Moreover, each agent represents a producer, consumer, or regulator, autonomously negotiating energy trades, balancing supply and demand, and optimizing grid stability. As a result, this decentralized network increases resilience and efficiency by preventing overloads and ensuring fair price adjustments in real time.
Such multi-agent architectures facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, reducing reliance on traditional centralized utilities and promoting cleaner energy use. In addition, agents monitor compliance with energy regulations and provide transparent transaction records, making the system trustworthy and scalable.
Use Cases of Multi-Agent Systems
Beyond industry examples, MAS is driving innovation in the best workflow automation software across sectors.
-
IT Service Management
In IT service management, MAS automates incident detection, ticket routing, and issue resolution with minimal human intervention. Agents monitor network health for signs of cyberattacks—including defending against a distributed denial-of-service attack—and then coordinate response actions in real time. This boosts system reliability and frees IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks.
-
Customer Support
Multi-agent chatbots collaborate to handle complex customer inquiries by distributing topics among specialized agents—billing, tech support, or account management. Consequently, this reduces wait times and increases resolution rates, enhancing user experience with human-in-the-loop checks for sensitive cases.
-
Legal and Compliance
Legal industries use MAS to process massive document volumes for contract analysis and compliance monitoring. Agents extract key data, flag potential issues, and update teams on regulatory changes. As a result, the automation of such tasks minimizes human error and expedites artificial intelligence implementation across demanding workflows.
Key Benefits of Multi-Agent AI in Enterprise Automation Solutions
- Scalability and Flexibility
Unlike a monolithic application, MAS enables enterprises to scale automation easily by adding or upgrading individual agents without disrupting entire workflows. This modularity supports incremental deployment and ongoing optimization.
-
Robustness and Fault Tolerance
Because agents operate independently yet collaborate, MAS maintains high availability—if one agent fails, others compensate. This decentralized network design is vital for mission-critical processes requiring uninterrupted IT operations.
-
Enhanced Autonomy and Decision Making
Agentic AI systems empower autonomous decision-making with AI reasoning that accommodates real-time data and context. As a result, this accelerates AI workflows, enabling businesses to adapt swiftly to market changes.
-
Improved Collaboration
Multi-agent systems embody collaborative intelligence, allowing agents to negotiate and share knowledge. This teamwork translates into more intelligent automation that mirrors human problem-solving capabilities, but at a much greater scale and speed.
Check out: AI vs Automation: Decoding the Differences for Business Success
Challenges and Risks of Multi-Agent Systems
Here are the challenges and risks listed below:
- Communication Complexity
Coordinating multiple autonomous agents can lead to bottlenecks or conflicting actions if communication protocols aren’t robust. Designing clear roles and efficient message exchanges is crucial to preventing these issues.
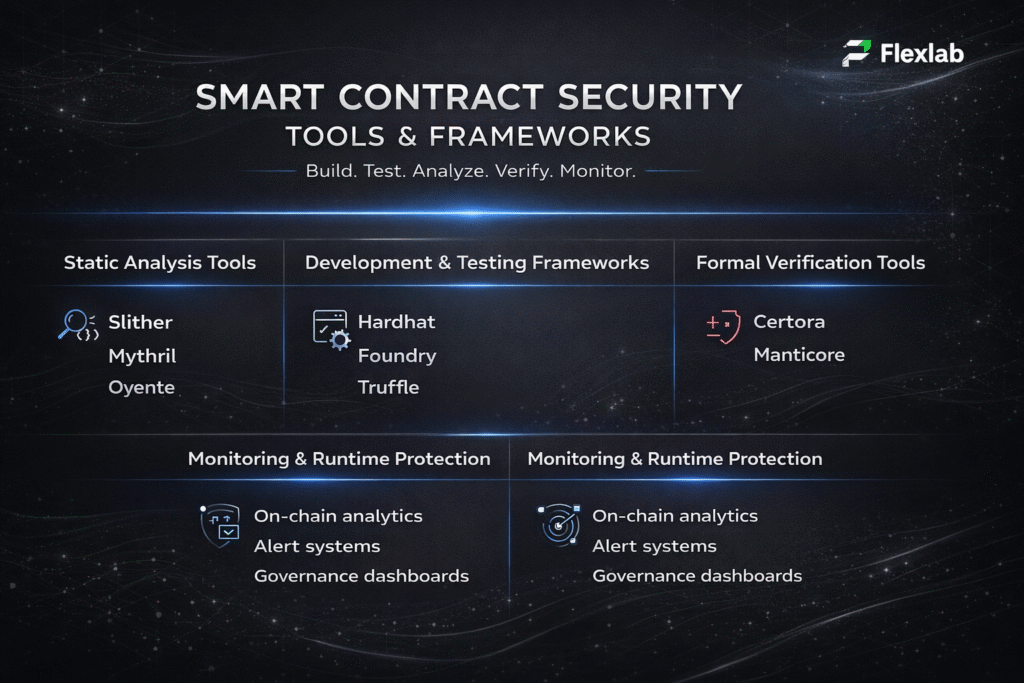
- Security Vulnerabilities
The distributed nature of MAS can expose enterprises to cybersecurity risks, including potential entry points for attacks like distributed denial of service. Therefore, continuous monitoring and advanced protective strategies are mandatory.
- Managing Human Oversight
While MAS automation is powerful, incorporating human-in-the-loop remains necessary in sensitive operations to ensure ethical decision-making and manage unpredictable scenarios effectively.
- Technical and Resource Demands
Multi-agent systems require significant expertise in AI software development and AI consulting services to design, deploy, and maintain, especially when integrating emerging technologies like large language models and reinforcement learning.
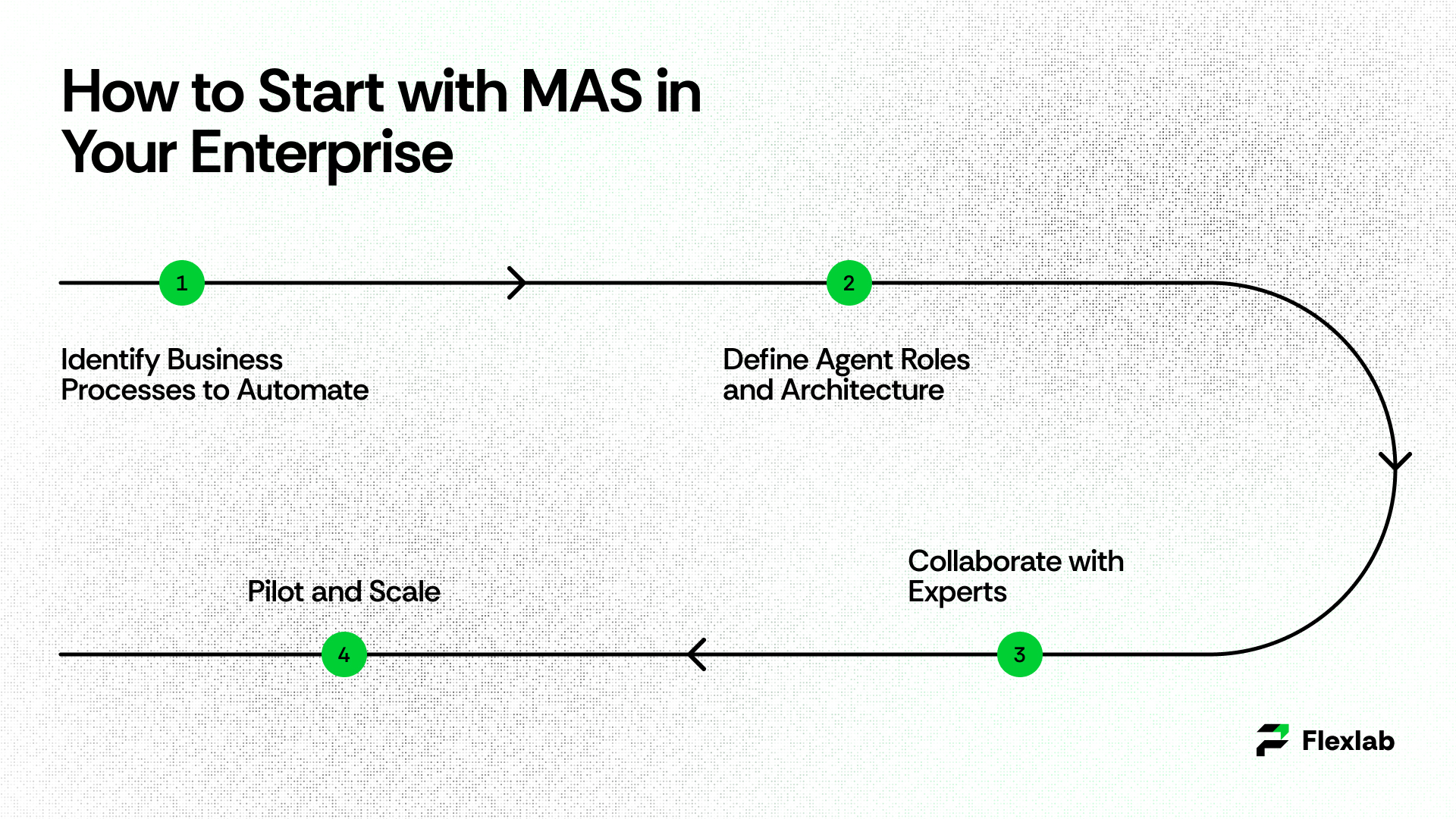
How to Start with MAS in Your Enterprise
Explore the step-by-step process below:
Step 1: Identify Business Processes to Automate
Start by mapping the processes that can benefit most from intelligent automation, such as supply chain optimization, IT service management, or customer workflows.
Step 2: Define Agent Roles and Architecture
Break down tasks into agent-specific functions with clear communication channels. Decide whether to use a centralized or decentralized network model depending on workflow complexity.
Step 3: Collaborate with Experts
Partner with providers of AI development services and AI consulting services to customize solutions. Tailored implementation of AI ensures MAS fits your unique enterprise requirements.
Step 4: Pilot and Scale
Deploy workflow automation software incrementally, monitor performance, and gather feedback. Then, use reinforcement learning and agentic AI system capabilities to evolve agent effectiveness over time.
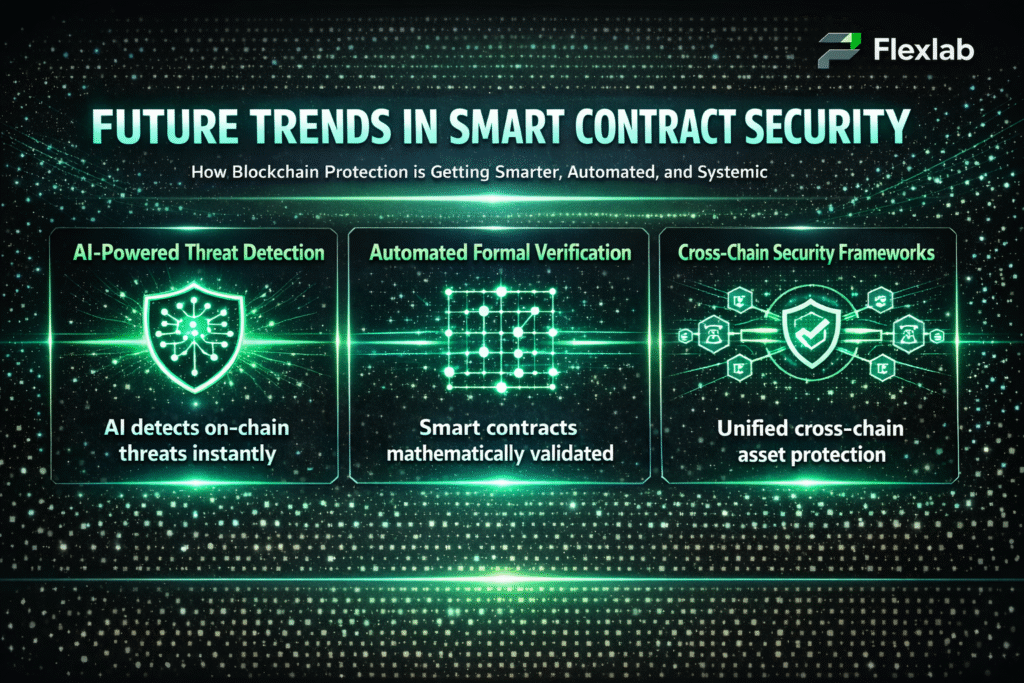
Future Trends for Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems are set to become increasingly important across industries. Major trends include:
- Greater collaboration with human teams, where agents support complex decision-making, boosting productivity and ensuring more accurate, ethical outcomes through human-in-the-loop approaches.
- Real-time optimization of supply chains and logistics, with agents dynamically coordinating routes and resources to improve efficiency and reduce disruptions.
- Wider use in smart city projects, helping monitor infrastructure and public services, while working alongside human overseers for safer, more efficient urban management.
Multi-agent systems represent a major shift in artificial intelligence and large language model use, enabling decentralized collaboration and autonomous decision-making at scale. They offer benefits like scalability, flexibility, and resilience, but also bring challenges around coordination, communication, and cybersecurity.
Moreover, advances in coordination protocols, hierarchical management, and security—especially against threats like distributed denial of service attacks—will unlock new possibilities for intelligent automation and AI workflows. As technology evolves, MAS will play a key role in solving complex global challenges such as healthcare, autonomous vehicles, and cybersecurity. Moreover, by combining adaptability, efficiency, and human oversight, multi-agent systems will continue to advance. The future looks bright, driven by ongoing innovations in AI and connectivity.
Ready to Transform Your Business with Multi-Agent Systems?
If you’re looking to unlock the full power of intelligent automation, Flexlab is your top U.S. partner for advanced AI agent guides and multi-agent system development. Our expert team specializes in custom AI solutions that bring collaborative intelligence and autonomous decision-making directly to your enterprise workflows. Flexlab provides scalable, resilient systems tailored to your unique needs. Specifically, these include supply chain optimization, workflow automation software, AI fraud detection, and cybersecurity.
Whether you’re new to AI or upgrading your automation, our AI consulting services provide the expertise you need. They also offer the guidance necessary for smooth implementation.
Don’t just keep up with the future—lead it. Visit our website to see how our multi-agent AI systems can supercharge your business, view inspiring projects in our portfolio, or reach out directly through our contact us page to start your transformation today.
Ready to Grow Your Business?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email us: info@flexlab.io
Concluding Insights on Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems represent a powerful shift in enterprise automation by combining autonomous, specialized agents into intelligent, collaborative networks. Their ability to scale, adapt, and work together surpasses traditional monolithic systems, making them essential for supply chain optimization, IT operations, AI fraud detection, and much more.
Though challenges remain, careful planning and expert support through AI development and consulting services can ensure smooth implementation. Forward-thinking enterprises adopting MAS today are setting the foundation for smarter, more resilient digital ecosystems tomorrow.
Unlock Expert Insights:
- 2025 Guide to Blockchain Development: Tools, Trends & Strategies
- Beginner’s Guide: How to Choose the Right AI Development Company
- Blockchain App Development: The Complete Guide for Businesses
<p>
A multi-agent system consists of several intelligent agents that work independently but collaborate by communicating and coordinating their actions. These agents solve complex problems together, tasks that would be too difficult for a single agent alone. By sharing information and dividing work, they improve efficiency and scalability. This approach is especially useful for dynamic environments where adaptability is key.
Popular multi-agent frameworks include AutoGen (by Microsoft), CrewAI, LangGraph, JADE (Java Agent Development Framework), Mesa (Python), and Ray (Python). Each framework provides unique tools and capabilities for designing, managing, and scaling multi-agent systems. Moreover, these options offer flexibility across languages and use cases, helping developers choose the best fit for their needs.
Implementing a multi-agent system starts with selecting the right framework for your goals. Then, clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each agent to ensure smooth cooperation. Testing the system’s scalability and behavior under different conditions is crucial. Finally, refine agent interactions continuously to build a robust, adaptive system. What is the multi-agent system approach?
What are the most popular multi-agent frameworks?
How to implement multi-agent systems?
























6 Responses
Very helpful content, learned a lot from this.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
With havin so much content and articles do you ever
run into any problems of plagorism or copyright infringement?
My website has a lot of completely unique content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all
over the web without my authorization. Do you know any ways to
help reduce content from being ripped off? I’d genuinely appreciate it.
Also visit my web blog – заказать микроавтобус мерседес