Role of Public Key Vs Private Key in Blockchain Security
Public and Private Keys | AI and Blockchain | Public vs Private Blockchain
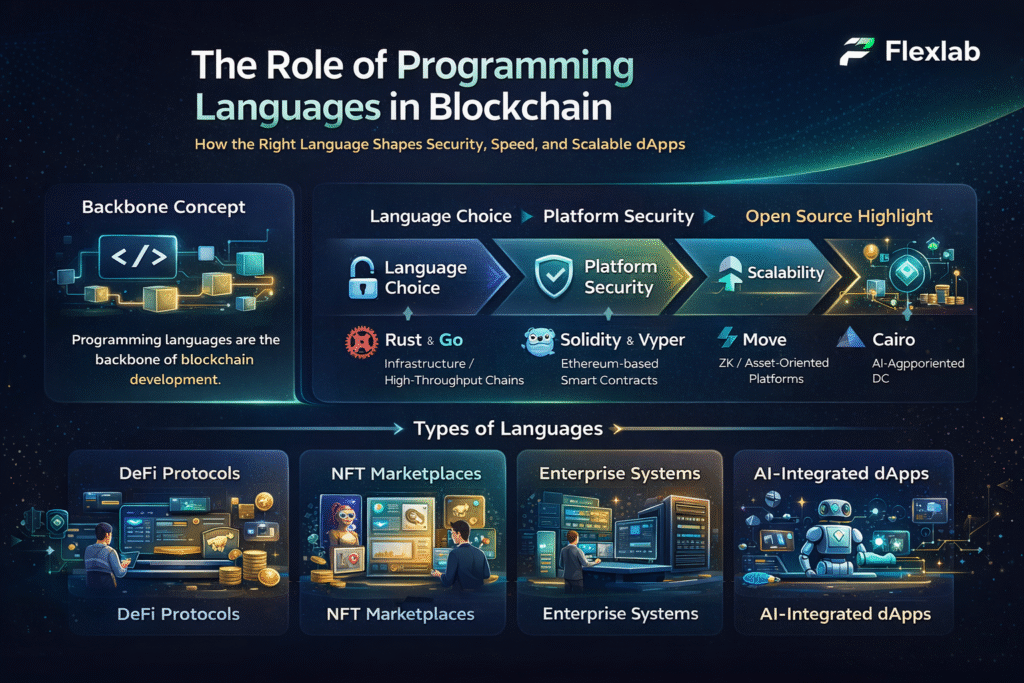
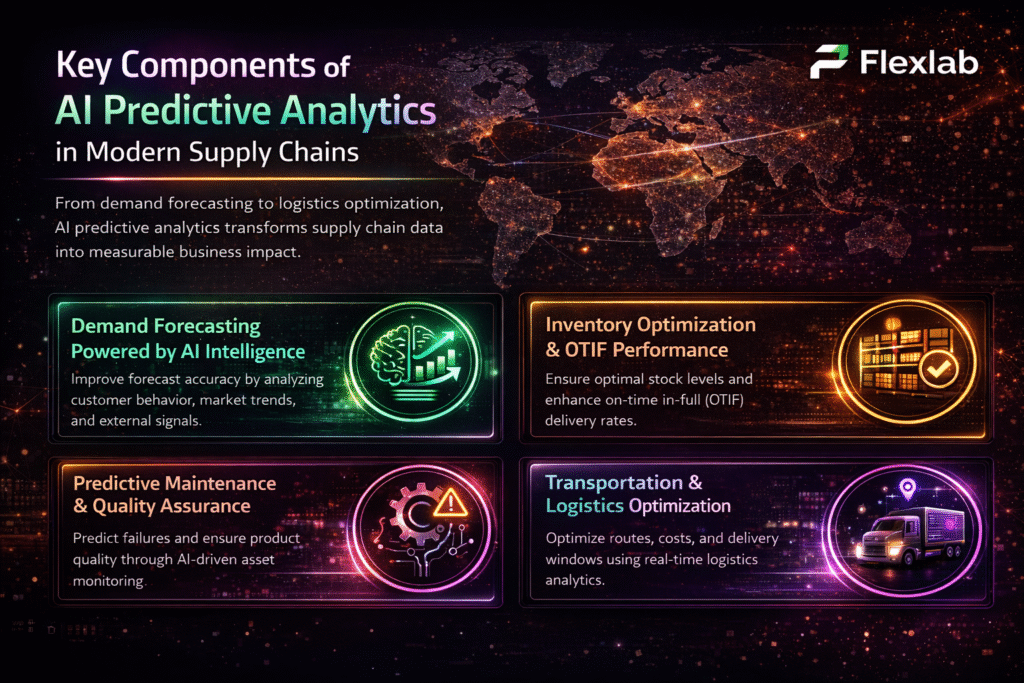
Public key vs private key is the foundation of blockchain’s “trustless” security model. Blockchain secures billions and even trillions of dollars in digital value without relying on centralized authorities. Instead, it uses cryptographic systems that ensure data integrity, ownership, and authenticity across decentralized networks.
Imagine sending a message in a locked box to someone across the world. If anyone copies the key, they can unlock the box and read the message. Early digital security relied on symmetric cryptography, where one shared key encrypted and decrypted data. Algorithms like AES and Data Encryption Standard (DES) use this method.
To overcome its limitations, asymmetric cryptography was introduced. Also known as public vs private key encryption, it uses two mathematically linked keys. The public key is shared openly, while the private key remains secure. Data encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted using its corresponding private key.
This blog will be your guide to what public and private keys are and how public vs private key works in blockchain security in detail.
Why Blockchain Needs Keys at All?
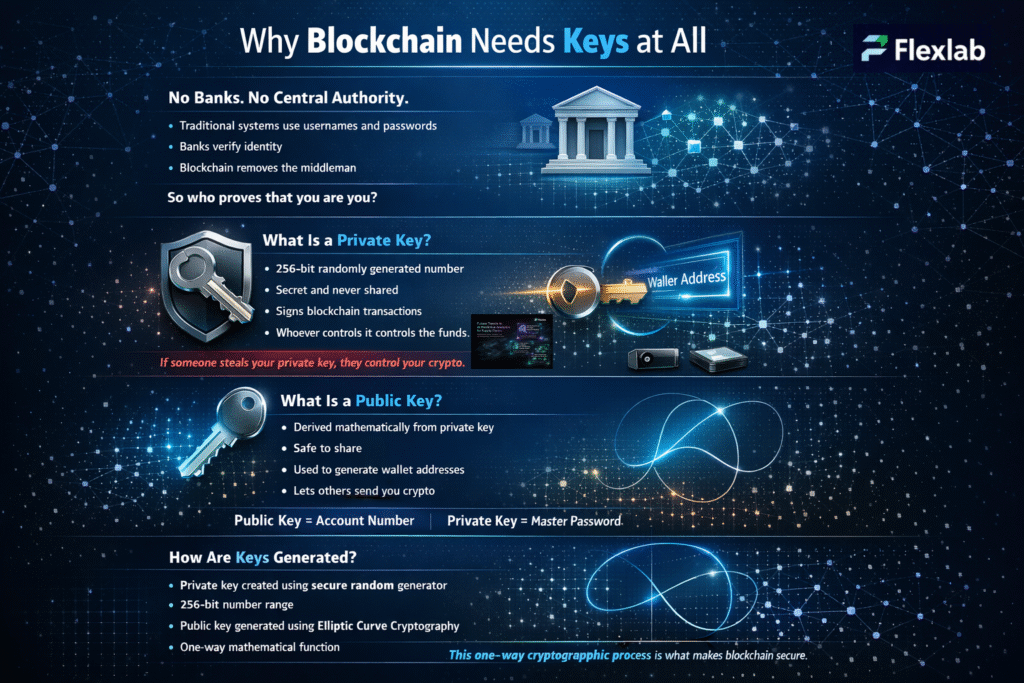
Traditionally, systems rely on usernames and passcodes, a central authority, and banks acting as guardians of identity. Blockchain networks remove this central server, also known as a bank. But then, who will verify your identity and prove that you are you?
It’s the cryptographic keys. Instead of logging into an account with a username and password, you prove your ownership by mathematically proving that you own a private key.
What Is a Private Key?
What is a private key? A private key is basically a randomly generated number, usually 256 bits long. It is a secret that is never shared and is the master key to your funds. If someone steals your private key, they control your crypto. A private key works like a password, but far more powerful. Anyone with the private key can access, transfer, or steal your digital assets. In blockchain security, the private key signs the transaction, and it helps verify that you are the rightful owner of a wallet address. Without your private key, you can never be able to recover your crypto funds. That is exactly why private keys can never be shared or stored online carelessly. Strong cryptocurrency security depends on protecting your private key using hardware wallets, offline backups, and encryption to prevent hacking, fraud, and irreversible loss.
What Is a Public Key?
What is a public key? A public key is mathematically derived from your private key. A public key is a cryptographic code that allows others to send you assets on a blockchain network. In the blockchain ecosystem, your public key is used to create wallet addresses that appear in cryptocurrency transactions. When someone transfers funds, they essentially use your public key-derived address to identify you as the recipient. Public keys are safe to share, and they act like your account number in digital wallets. Together with private keys, they guarantee secure verification, transparency, and trust without relying on middlemen.
How Are Keys Generated?
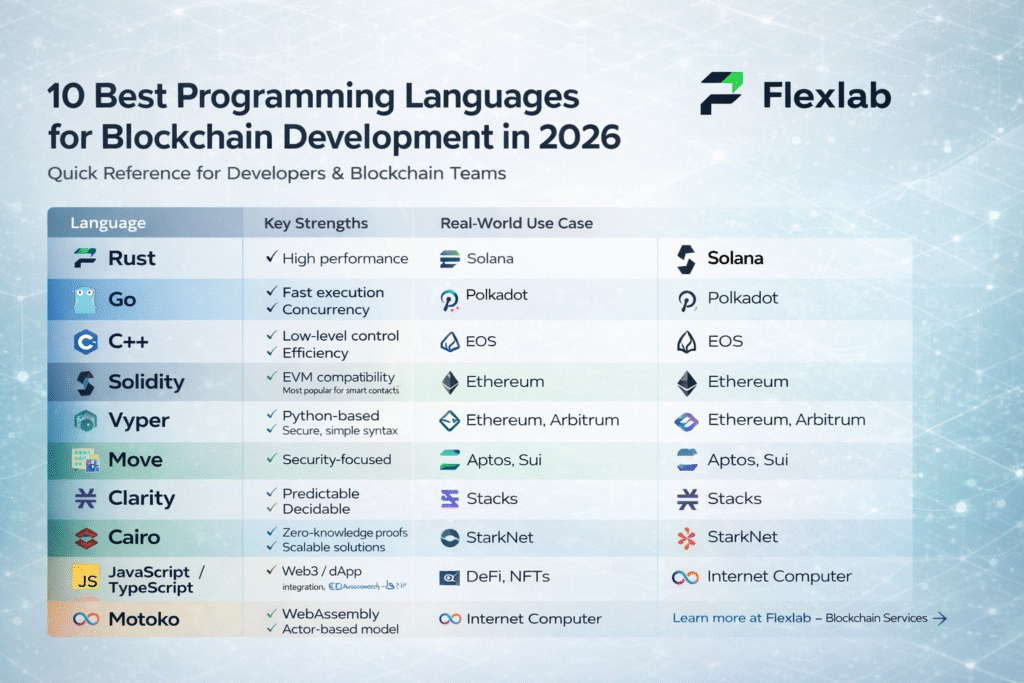
The keys discussed here are not really keys, but rather large prime numbers that are mathematically related to one another. In this case, “related” means that only the corresponding private key can decrypt data encrypted with a public key. A secure random number generator usually generates the private key. It contains a large range, typically 256 bits long. Therefore, the chance of two people having the same key is practically zero. In addition to this, a public key is created using Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). As its name implies, ECC depends on elliptic curves to generate keys. It is mostly used for key agreements and digital signature verification. This process is one-way, fast to compute forward. In addition to this, this process is impossible to reverse. This one-way creation process is what makes blockchain platforms safe.
How Keys Work Together in a Transaction?
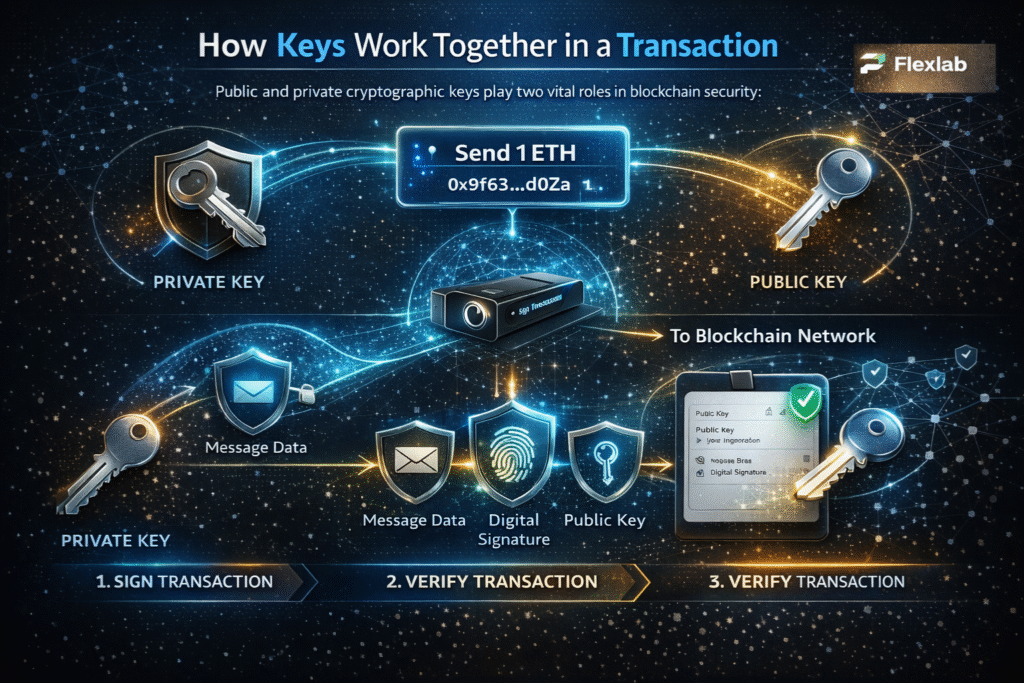
To really understand blockchain security, it helps to understand what happens when a transaction is created and verified. When you start a transaction, your wallet software constructs a message explaining or describing what you want to do. For instance, the message says ‘Send 1 ETH to this address.’ This message is then signed using your private key. Furthermore, the signing process constructs a digital signature, which is unique to both the message and the private key. Even changing one micro detail in the transaction will entirely change the digital signature.
Your transaction now contains the three most important elements;
- The transaction data or message
- Your public key (or something derived from it)
- The digital signature
When the transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network, blockchain nodes independently verify it. These nodes use your public key to verify whether the signature matches the transaction data. If it matches, the blockchain network knows the real owner approved the transaction.
In this process, you never reveal your private key. It stays safely on your device, while the system uses your public key to validate and verify your authority. Therefore, this process allows millions of strangers to agree on ownership without trusting each other or a central server.
Basically, public and private keys work like a digital lock-and-key system. This system helps guarantee that online communication and transactions remain safe, private, and trustworthy. These keys work in two major ways;
- Encryption & Decryption to keep the information private
- Digital signatures to prove identity and digital authenticity
Encryption & Decryption
Public and private keys ensure that the message reaches the intended recipient. When a user wants to share a private message with someone, they use their public key to encrypt that message; however, the receiver has to have their private key to decrypt that message. Even if someone other than the receiver intercepts the message, they would require the private key to decrypt or open that message. Encryption algorithms like RSA-OAEP and Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES) mostly use this method. Many secure websites (HTTPS), online banking platforms, and messaging apps also apply this hybrid approach.
Digital Signatures
Digital signatures prove that a specific sender sent the message and that no one has altered it. The sender uses their private key to create a digital signature, which is basically a unique stamp on the message. Afterwards, the receiver can verify that signature using your public key. If it checks out, they know two things. First, the message has been sent by you, and the message content has not been altered.
How Public and Private Keys Build Trust Without Trust?
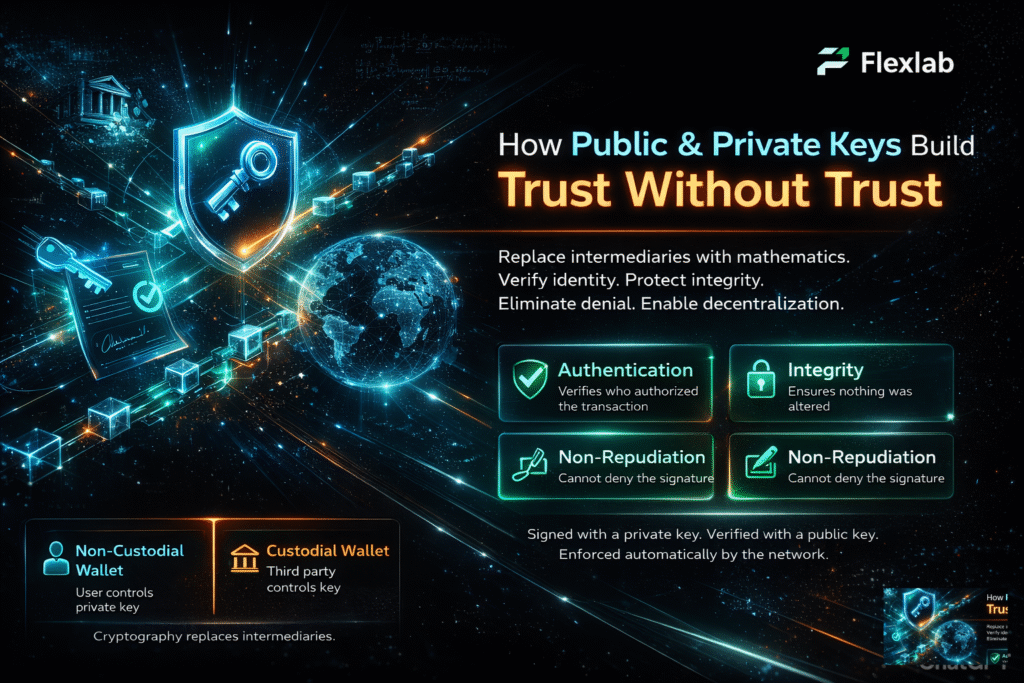
Traditional and old financial systems used to rely on intermediaries or banks to verify your identity and ownership. However, blockchain replaces those intermediaries with cryptography. Public and private keys create trust without trust by providing three major security properties;
- Authentication– They prove and verify who authorized a transaction.
- Integrity– They guarantee that the transaction hasn’t been altered.
- Non-repudiation– The signer or the owner cannot deny having signed the transaction.
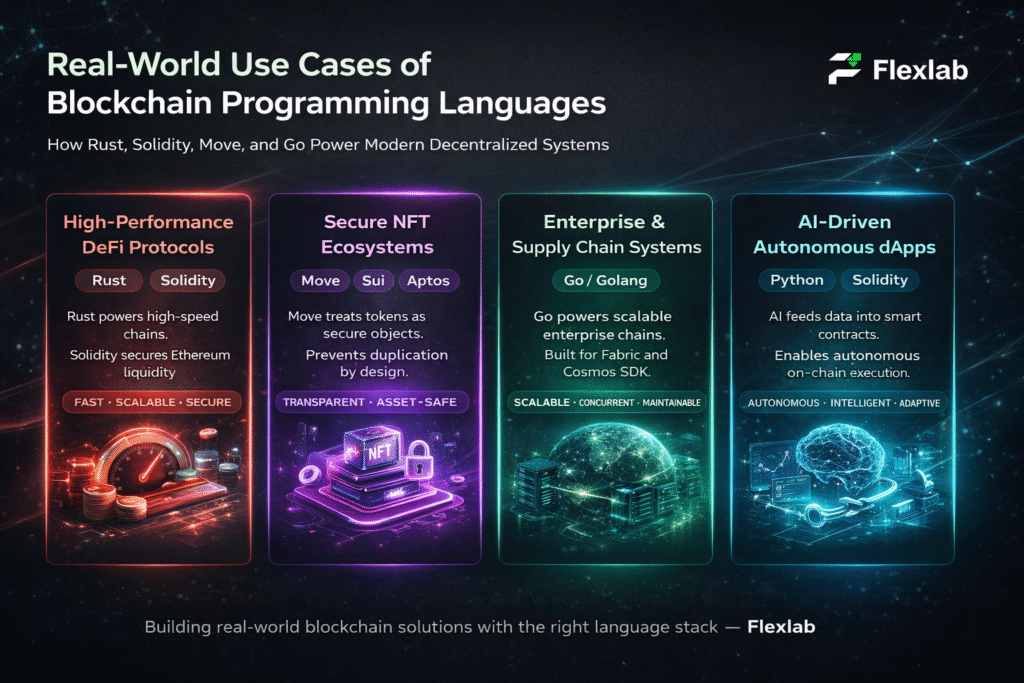
Every transaction or message uses a private key to sign it and a public key to verify it, allowing the network to enforce rules automatically without third-party approval. This is what enables decentralized finance, NFTs, DAOs, and smart contracts to operate globally and continuously. Instead of trusting institutions and humans, users trust maths.
Role of Keys in Wallets
When we talk about types of crypto wallets, the only word that comes to mind is custodial vs non-custodial wallet. How keys are stored and managed defines the security protocols of a wallet. When it comes to non-custodial wallets, the users control and manage the private keys themselves without trusting the middlemen. A non-custodial wallet simply helps generate, store, and use them. Consequently, the ownership solely belongs to the users. Examples include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Hardware Wallets like Ledger.
However, when it comes to a custodial wallet, a third party or intermediary holds the private key on behalf of the user. Several exchanges help users store their private keys.
Future of Public and Private Keys in Blockchain Security
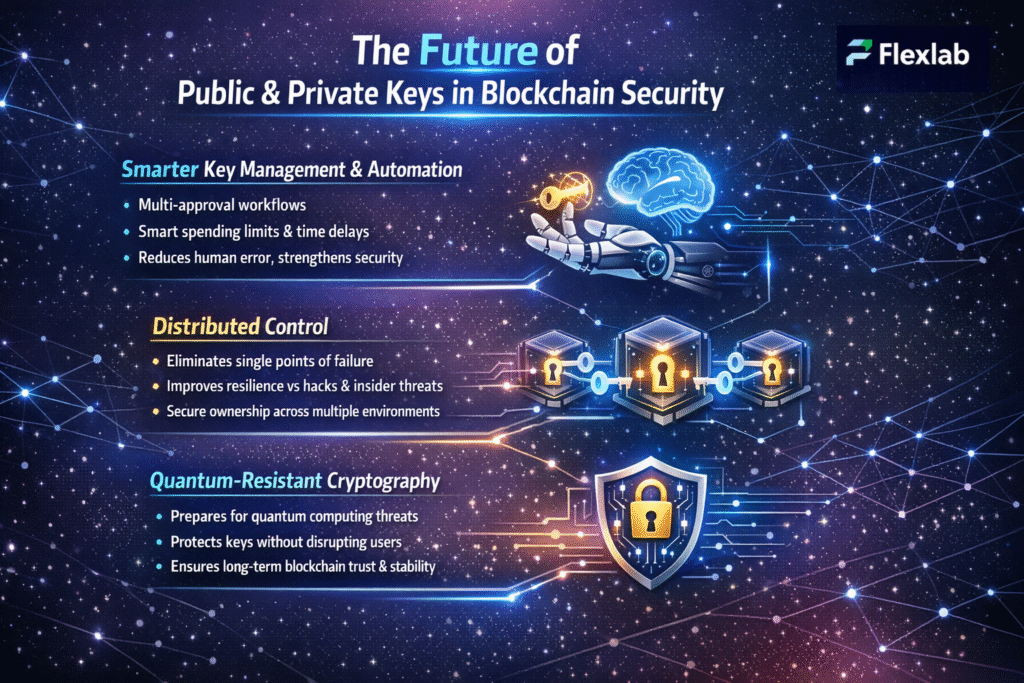
As blockchain technology continues to mature, the role of public and private keys is expanding beyond basic transaction security. Increasing adoption, growing transaction volumes, and evolving cyber threats push blockchain systems to rethink how they create, manage, and protect cryptographic keys. As a result, future blockchain security focuses not only on stronger encryption but also on smarter key control, improved resilience, and long-term sustainability.
Smarter Key Management and Automation
As blockchain adoption grows, key management is becoming more automated and intelligent. Instead of relying only on manual private key handling, future systems enforce security rules through programmable logic. As a result, transactions follow predefined conditions such as multi-approval workflows, spending limits, and time delays. This approach reduces human error while strengthening overall blockchain security.
Distributed Control to Eliminate Single Points of Failure
Future blockchain systems are moving away from storing private keys in a single location. Instead, they distribute control across multiple secure environments. Consequently, attackers cannot compromise ownership by accessing one system alone. This distributed model significantly improves resilience against hacks, insider threats, and operational failures.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography and Long-Term Security
Although today’s encryption remains reliable, future computing advancements introduce new risks. Therefore, blockchain networks are actively preparing quantum-resistant cryptographic methods. These upgrades protect public and private keys without disrupting existing users. By planning, blockchain platforms ensure long-term trust and system stability.
The Evolving Role of Public and Private Keys in Blockchain
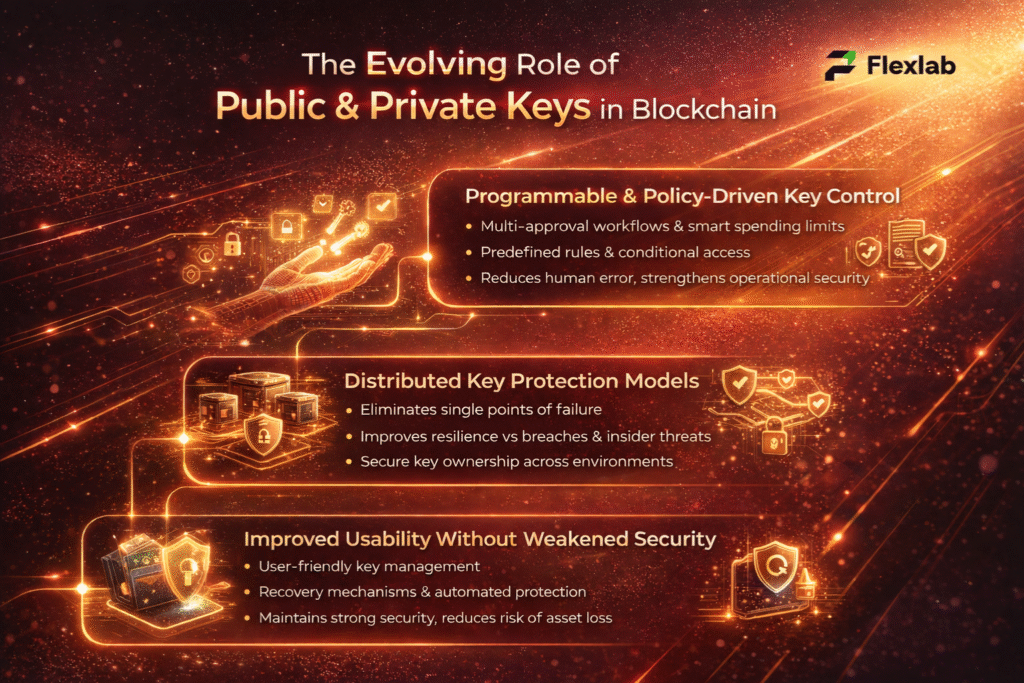
As blockchain systems continue to scale, public and private keys now play a broader role beyond basic transaction security. Modern blockchain networks actively improve how they control, protect, and apply keys across complex environments. As a result, key management is becoming more resilient, automated, and better suited for large-scale adoption.
Programmable and Policy-Driven Key Control
Rather than relying on a single private key for full authority, blockchain platforms now apply programmable rules to key usage. For example, transactions may require multiple approvals, spending limits, or predefined conditions. Consequently, this approach reduces human error while strengthening operational security without compromising decentralization.
Distributed Key Protection Models
To eliminate single points of failure, modern systems avoid storing private keys in one place. Instead, they distribute key control across multiple secure environments. Therefore, attackers cannot gain full access by compromising a single system. This model significantly improves resilience against breaches, insider threats, and operational disruptions.
Improved Usability Without Weakened Security
Blockchain wallets are evolving to make key management more user-friendly. Instead of placing the full burden on users, modern solutions introduce recovery mechanisms and automated safeguards. As a result, users can maintain strong security while reducing the risk of permanent asset loss or access errors.
Take Your Blockchain Security to the Next Level with Flexlab
Understanding public and private keys is just the beginning. Whether you’re building secure wallets, integrating blockchain into your business, or exploring cutting-edge AI and crypto solutions, Flexlab can help you make it happen.
Check out our portfolio to see how we’ve empowered businesses with secure, scalable blockchain and AI solutions. If you’re curious about what we can do for your project, contact us today. Discover the future of secure technology with Flexlab, where innovation meets trust.
Explore our full range of services or dive into more insights on our blog. Connect with us on LinkedIn to stay updated on the latest in blockchain, AI, and digital security.
Curious to dive deeper into blockchain, secure systems, and real-world applications? These reads will help you level up your skills and see how blockchain can truly transform businesses and careers:
- How to Become a Blockchain Developer?
- The Role of Blockchain Audit in DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 Security
- How Does Blockchain for Startups Improve Transparency and Trust?
Conclusion: How Public Key Vs Private Key Secures Blockchain
Public Key Vs Private Key encryption forms the foundation of blockchain security, ensuring that encrypted communication is safe and that identities are verified reliably. By using public keys to lock messages and private keys to unlock them, blockchain guarantees that only the intended recipient can access sensitive information.
These keys protect wallets and digital assets, and they also support scalable, efficient, and reliable blockchain systems. Moreover, understanding how public and private keys work together enables businesses and individuals to maintain trust, minimize risks, and confidently adopt decentralized technologies. As a result, proper key management strengthens security, ensures transparency, and allows blockchain networks to operate smoothly across global platforms.
Ready to Take Your Blockchain Security to the Next Level?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email Us: info@flexlab.io
FAQ’s
1: What is a key ceremony, and why does it matter in blockchain?
A key ceremony is a controlled process that securely generates and manages cryptographic keys in complex systems. In some blockchain setups, especially those using multiparty computation, participants create keys through a formal ceremony to ensure no single person ever controls the complete private key. This reduces the risk of leaks or insider threats and strengthens trust in environments with high security requirements.
2: Can blockchain use temporary keys instead of permanent ones?
Yes, some advanced systems use transient-key cryptography, where they create key pairs for short time intervals and then destroy them. These temporary keys help timestamp and secure data without long‑term key exposure and can support features like forward secrecy. This approach can improve security for certain time‑sensitive applications on or alongside blockchains.
3: How do public keys relate to decentralized identities outside wallets?
In decentralized identity systems, a decentralized identifier (DID) links an identity to one or more public keys in a verifiable document. Instead of traditional usernames and passwords, these public keys help confirm identity and allow authentication across Web3 applications. This approach gives users more control over their digital identity without relying on central authorities.