What Are NFTs and How Do They Create Value?
Multi-Agent Systems | Web3 Technology | AI Development Company
In recent years, NFTs have gone from a niche concept in blockchain experimentation into a cultural and economic trend. They have sparked debates, inspired creativity, and shown new ways of owning and trading digital collectibles. NFTs are one-of-a-kind digital tokens with distinct features that cannot be divided, replicated, or substituted.
In this blog, you will explore what exactly NFTs are, what NFTs are used for, and how they work in real life. This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of NFTs, exploring their functionality, applications, real-life use cases, and much more.
What are NFTs?
You must be curious what NFTs are. What does NFT stand for? NFT stands for non-fungible token. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are digital assets such as artworks, digital content, or videos that have been stored and tokenized through blockchain technology. In simple words, NFT means something unique and non-replaceable. One cannot exchange an NFT on a one-to-one basis with another item because it is unique and special. In contrast, physical money or cryptocurrencies are fungible, meaning they can be traded and exchanged for one another. For example, a dollar bill is fungible because every single dollar has the same worth. On the other hand, a Coldplay concert ticket is non-fungible because its value is specific to its rarity. Every NFT contains a unique digital identity, which makes it distinct from others.
The second part of the term “token” means a digital signature or certificate stored on a blockchain that indicates ownership. Tokens are basically unique identification codes generated from metadata via an encryption function. This connection between the token and asset is what makes an NFT special.
As a result, an NFT is a digital certificate of authenticity and ownership. It is a verification that a digital asset– whether a painting, an artwork, a song, a video, or even a tweet is original and belongs to a specific individual.
How Do NFTs Work?
How do NFTs work? Here you go with your answer to this question. NFTs operate on distributed ledger technology, the same blockchain technology that powers cryptocurrencies. However, cryptocurrencies are interchangeable, while NFTs are unique and non-exchangeable. How to mint an NFT? NFTs are basically created through a process named ‘Minting’, in which the asset’s information is stored on a blockchain. When someone mints an NFT, they are embedding a unique digital signature into the blockchain, proving ownership and authenticity. This process of minting involves incorporating smart contracts that assign ownership and facilitate the management of NFT transfers. Blockchain technology then stores the transaction history and ownership of each NFT, guaranteeing that the information remains secure and immutable. This enables users to verify the authenticity and provenance of an NFT, as well as track its ownership back to the creator.
Once created, NFTs can be listed for sale on online marketplaces such as OpenSea, Rarible, and Foundation. Buyers can buy them using cryptocurrency, most popularly Ethereum, available in PlasBit Crypto wallets. The blockchain permanently stores the record of transaction history, ensuring that anyone can trace ownership back to the rightful holder. Once someone buys an NFT, the buyer’s digital wallet records it, enabling connection to various Apps and platforms for display and further trading. Unlike traditional digital assets, which people can copy endlessly, no one can duplicate an NFT, making it a one-of-a-kind asset.
Discover more about: Blockchain and IoT: Benefits, Use Cases, and Their Challenge
What Makes NFTs Unique?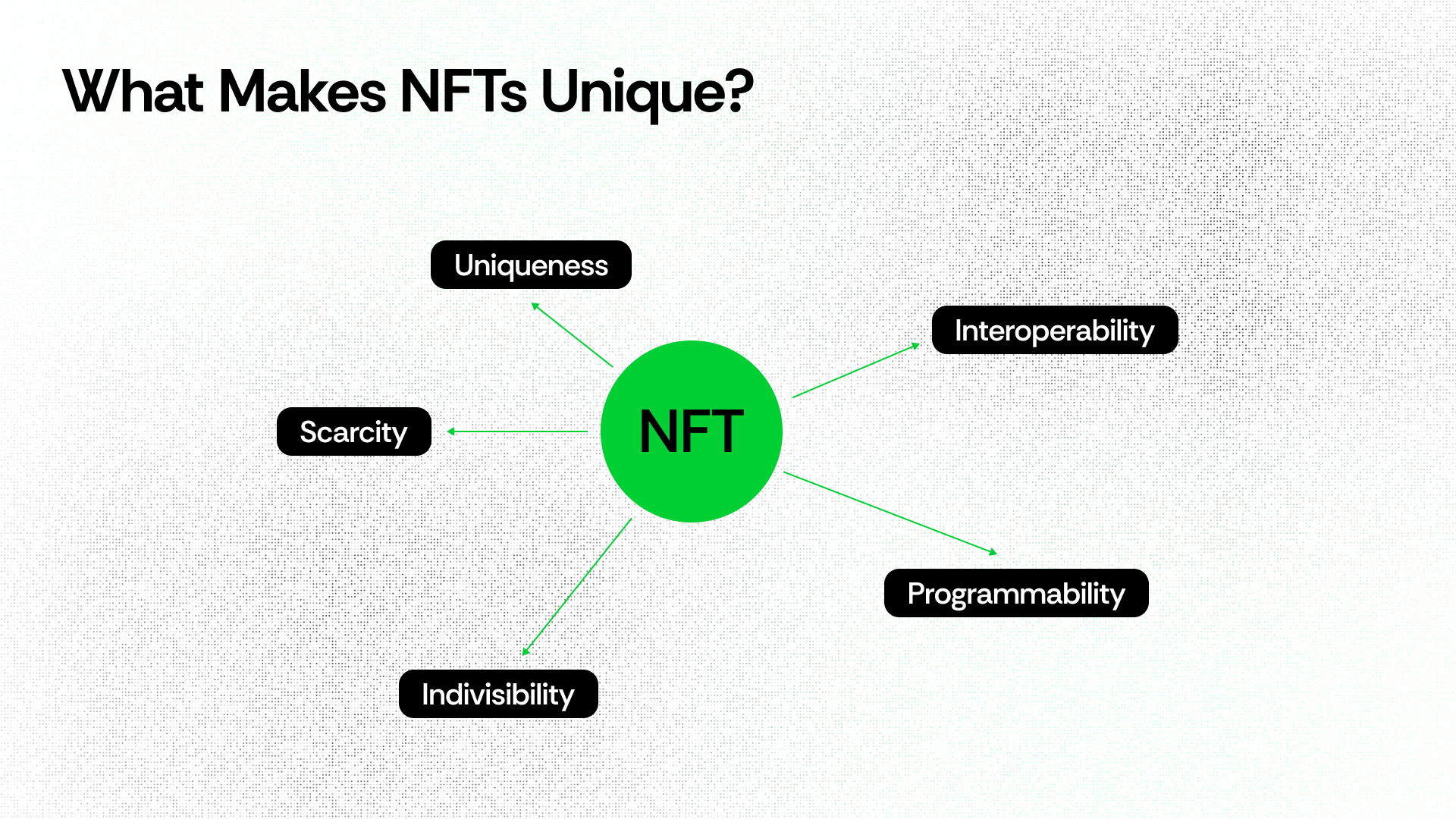
One of the most significant NFTs key features that makes them special is their uniqueness. Each NFT possesses its own digital signatures that distinguish it from others. This uniqueness is what makes an NFT rare and valuable in the digital world. Scarcity is another feature that makes NFTs special, since creators can choose to issue only a limited number of digital tokens to their work. This limited supply often drives up the demand, making an NFT scarce.
Indivisibility is another significant feature that makes an NFT valuable. Unlike cryptocurrencies, which users can split into smaller units, NFTs remain whole, making them unique. In addition, NFTs maintain interoperability, allowing users to trade them across different platforms and marketplaces. However, the most revolutionary feature of an NFT is its programmability. For instance, users can embed specific rules in smart contracts, such as earning a royalty whenever their NFT is traded or resold.
Blockchain and Fungibility
Similar to physical money, cryptocurrencies are fungible from a financial perspective, meaning that one can trade and exchange them for one another. For example, one bitcoin always has the same worth as another bitcoin at a given exchange. This fungible nature of cryptocurrencies makes them suitable as a secure medium of transaction in the digital economy.
However, with the help of blockchain, NFTs have shifted the crypto paradigm by characterizing each token as unique and immutable. This makes it impossible for one non-fungible token to be equal to another, hence providing the proof of ownership. NFTs basically represent digital assets, and people associate them with digital passports because each digital token carries a unique and non-transferable code that distinguishes it from other tokens. On the other hand, NFTs are also extensible, meaning you can combine one with another to create a new NFT. This process is often called “breeding”.
Real Life Use Cases of NFTs
What are NFTs used for? Although NFTs are typically associated with digital art, their applications go far beyond that field. Here is your guide to some of the important NFT use cases;
- Art World
- Music Industry
- Gaming Industry
- Virtual Real Estate
- Collectibles and Physical Assets
-
Art World
In the art world, NFTs have established a wonderful avenue for artists to display and sell their work. Digital artists who have a long history of struggle to monetize their creations can now showcase their work and sell NFTs directly to buyers. For example, in 2021, an artist named Beeple sold his digital collage, Everydays: The First 5000 Days, for USD 69 million at an auction. Contrary to traditional art sales, NFTs also allow artists to keep earning royalties whenever collectors resell their artwork in the future.
-
Music Industry
In the music industry, singers and musicians can use NFTs to sell their albums, singles, or exclusive fan experiences to their audience. Instead of relying on streaming platforms, which often pay very little per play, artists can directly connect with their audience through NFTs. Musicians can now tokenize their work, granting buyers the rights the artists want them to have. For example, the band Kings of Leon once sold one of their albums as an NFT. It included exclusive perks for their fans, such as limited-edition vinyl and front-row concert tickets.
-
Gaming Industry
NFTs are gaining popularity in the gaming industry as well. Gamers can now purchase, sell, or trade in-game items such as skins, characters, or weapons as NFTs. Unlike conventional games that lock digital assets within the game itself, NFTs let users own and transfer these assets across different platforms. Web3 gaming is a common use case of NFTs. Axie Infinity is a popular example of an NFT-based game. In this game, players can breed, trade, or battle NFT creatures that can have real-world monetary value.
-
Virtual Real Estate
Another exciting use case or application of NFTs is virtual real estate. NFTs can represent ownership of virtual properties, structures, and land within the virtual world and metaverse. Decentraland or The Sandbox are examples of blockchain-based virtual real estate. Therefore, this allows users to buy, sell, and develop these virtual properties, building unique experiences and making income through in-world events.
-
Physical Assets and Collectibles
Beyond entertainment, users are exploring NFTs in the field of physical assets such as luxury goods, sports memorabilia, etc. This enables users to verify the authenticity of these items and easily trade ownership through digital means.
NFTs have given rise to a new generation of digital collectibles, from virtual trading cards to digital pets. Users can buy, sell, or trade these items across various platforms, and some rare NFT collectibles can bring excellent prices.
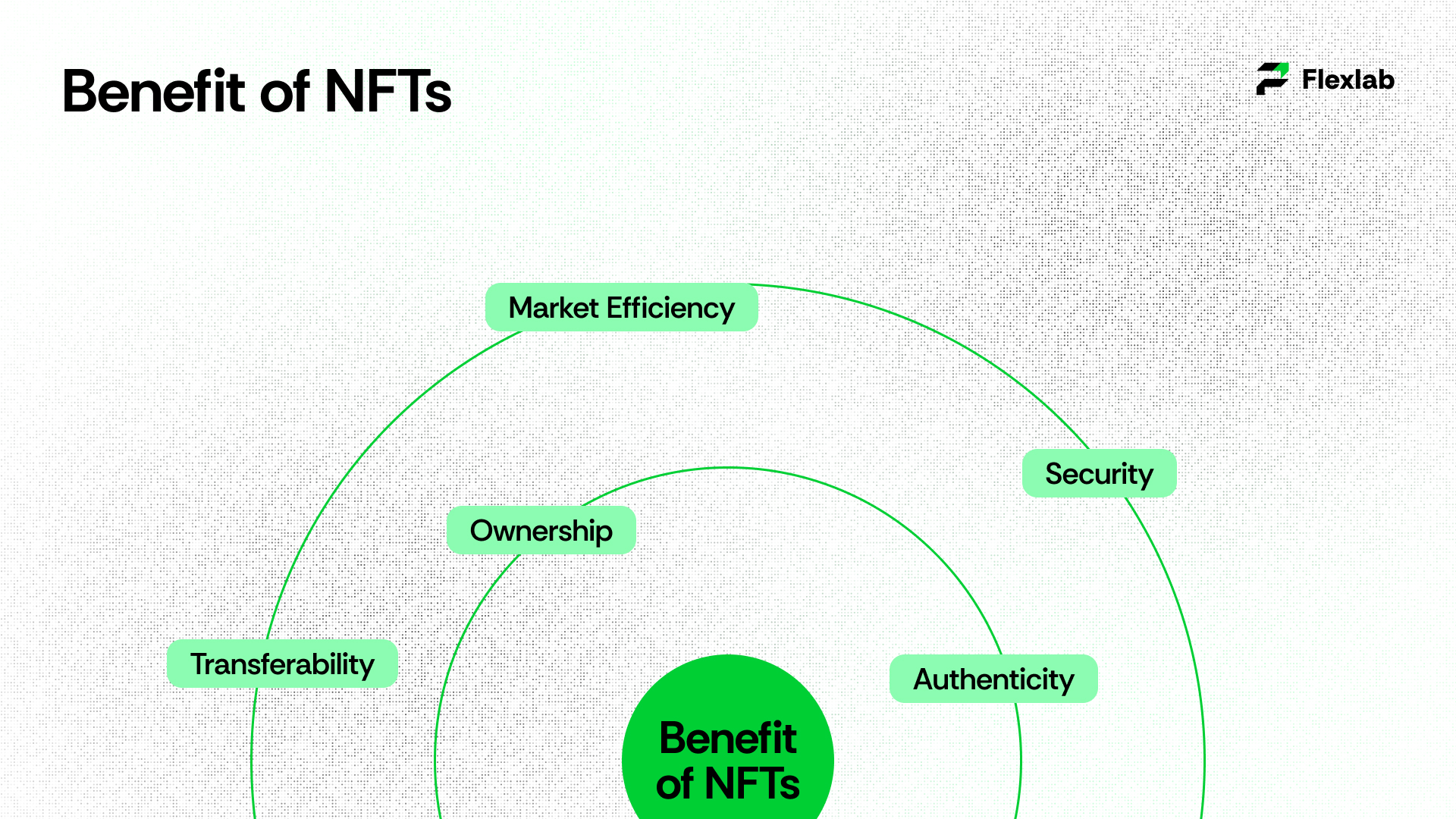
Benefits of NFTs
Built on distributed ledger technology, it is a digital token that represents the ownership of a digital asset. The following are the benefits of NFTs;
- Ownership
- Authenticity
- Transferability
- Market Efficiency
- Security
1. Ownership
The primary benefit of NFTs is that they give the buyers proof of ownership. NFTs can help associate ownership with a single creator as they are recorded on blockchain nodes. NFTs remain indivisible, and no one can share them among multiple owners.
2. Authenticity
NFTs have unique codes stored on the blockchain to enhance their authenticity. The immutable nature of blockchain records ensures that one cannot alter or duplicate NFTs. This feature enhances the authenticity of assets by making it easy to distinguish the original from copies. Also, this significant feature of NFTs demonstrates their ability to add value.
3. Transferability
Because blockchain technology powers NFTs, smart contracts simplify ownership transfers. Users can easily buy, sell, and trade NFTs across various marketplaces and platforms. In addition to this, the smart contract-based transfers are secure and efficient with minimal intermediaries, enhancing accessibility and market liquidity.
4. Market Efficiency
By tokenizing digital assets, NFTs can streamline transactions with minimal intermediaries and automate ownership transfers through smart contracts. This makes buying and selling of NFTs simpler, faster, and more efficient, enhancing market efficiency and transparency.
5. Security
Furthermore, non-fungible tokens play an important role in identity security. For instance, an immutable decentralized ledger stores personal information, and without the keys or passcode, no one can access, steal, or use it. Therefore, NFTs enhance the protection of digital assets and the privacy of owners.
What is an NFT Marketplace?
The NFT landscape is evolving continuously; however, typically, most of the best NFT marketplaces fall into these three categories;
- Open Marketplace: Anyone, regardless of background, can buy, sell, or mint an NFT. Open marketplaces can mint NFTs for you, though users can also mint their own work.
- Closed Marketplace: Buying, selling, or trading is restricted in closed marketplaces. Artists need to apply and platforms that approve them to trade virtual assets, ensuring exclusivity and curated quality.
- Proprietary Marketplace: It is a platform owned and operated by a specific company, where NFTs are created, sold, or traded under its trademark. It often restricts transactions to its ecosystem, guaranteeing brand consistency and revenue retention.
Some of the examples of NFT marketplaces include OpenSea, Foundation, NBA Top Shot, Nifty Gateway, and Rarible.
Unlock the Future of NFTs with Flexlab
NFTs have been very transformative in how we think about ownership, creativity, and authenticity in digital space. However, creating a secure and scalable NFT project requires the right expertise. Flexlab is your go-to partner for building a secure and authentic NFT project. With our team of experts, we turn your bold ideas into realities through our blockchain and smart contract development and cryptocurrency solutions. Whether you are an artist or a business owner, looking to launch NFT collections, marketplaces, or an innovative digital experience, our team can craft custom solutions to bring your vision to life.
Flexlab makes sure your NFT project is reliable, future-ready, and designed to stand out in the fast-growing digital space. Visit our portfolio to have a look at our services.
Want to have an in-depth knowledge of different topics such as AI Automation Tools, Cybersecurity Risk Assessment, and Blockchain App Development? Have a look at our blog page to have detailed and clear insights.
Ready to Grow Your Business?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email us: info@flexlab.io
Bottom Line on What are NFTs?
Concludingly, in this constantly evolving digital era, NFTs represent a groundbreaking shift in how we think about ownership. They provide users with new ways to earn money, buyers with authentic assets, and companies with innovative business models. However, at the same time, they raise critical concerns about legality, sustainability, and accessibility.
By integrating blockchain technology into music, art, sports, fashion, and more, NFTs offer an innovative way to make assets unique and valuable. What started as an experiment in blockchain technology is now reshaping the future and changing how we value digital content. In real life, NFTs are not just collectibles—they are a peek into the future of ownership, creativity, and commerce.
Are NFTs a good investment?
NFTs can be a good investment for those who understand the market, as they offer unique ownership of digital assets, including art, music, and games. However, their value is highly speculative and depends on demand, trends, and community interest. Opposite to traditional assets, NFTs lack stable regulations and can be very volatile. Therefore, they should be approached cautiously and as part of a diversified investment strategy.
Are NFTs better than cryptocurrencies?
NFTs are not necessarily riskier or safer than other cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. They both have their own set of pros and cons, such as working on a decentralized network and being subject to volatility. So, their value depends on the user’s goals and risk tolerance.
What file format is best for an NFT?
The best file format for an NFT depends on the type of digital asset being created. For images, PNG and JPEG are most popular because of quality and compatibility, while GIF goes well with animations. For 3D art, GLB or MP4 formats are commonly used, and MP4 is also standard for video NFTs. Concludingly, the ideal format balances high quality, small file size, and broad marketplace support.



























5 Responses
Very helpful content, learned a lot from this.