How Public and Private Keys Work: A Detailed Breakdown
Blockchain Trends | Digital Transformation Strategy | Private Blockchain Development
Public and private keys form a pair of mathematically linked numbers that help protect information in cryptography. You can share the public key with anyone and use it to lock or encrypt messages. The owner keeps the private key secret and uses it to unlock or decrypt those messages. Together, they create a secure way to communicate, with the private key also used to make digital signatures that the public key can verify. This system ensures that only the intended recipient can read the message and confirms the sender’s identity, enhancing overall digital security.
Do you know that public and private encryption keys are gaining popularity? Their adoption increased from 45% in 2023 to 58% in 2025. Growing concerns about cybersecurity risk assessment and the need for secure digital communication drive this rise. Let’s read more detailed insights below.
What are Encryption Keys?
Encryption keys are special strings of characters that lock (encrypt) and unlock (decrypt) data, ensuring that only authorized people can read it. Think of a key like the key to a door: it secures the data (like locking the door) so no one else can access it without the right key. This technology is widely used in crypto wallets, which rely on robust key management to secure users’ assets.
There are different types of encryption keys. Some keys act as shared secrets that both the sender and receiver use to scramble and unscramble messages. Others work as key pairs: anyone can use the public key to lock the data, and only the owner uses the private key to unlock it.
These keys protect information during transmission or storage, ensuring that only the intended people can access the original message or data. Moreover, encryption uses complex mathematical algorithms to ensure the security of the encrypted content. Let’s break down the algorithms below. This is especially important for blockchain address protection and the validation of crypto transactions.
Cryptographic Algorithms
Let’s read some mathematical cryptographic algorithms that are used to generate the public and private keys.
-
- Rivest-Shamir-Adelman (RSA)
- Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) is the oldest public-key system. It’s usually used to send shared keys for other types of encryption.
Digital Signature Standard (DSS) is a government standard that sets the rules for how to create digital signatures. NIST uses it to make sure signatures are done securely.
Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) uses special math with elliptic curves to create keys. It’s often used to agree on keys and make digital signatures.
These methods operate under the public key infrastructure model. They help secure various systems, including a virtual private network (VPN), and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. All of these encryption methods can generate asymmetric key pairs of various sizes.
Types of Encryption Keys
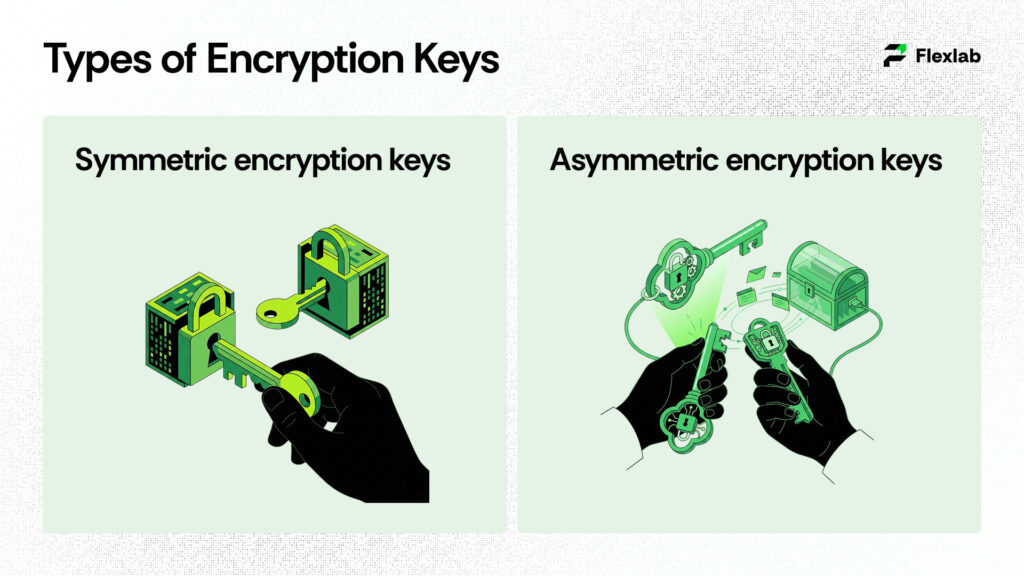
There are two cryptographic approaches that are designed to solve specific security issues. Let’s read below.
- Symmetric encryption keys
- Asymmetric encryption keys
Symmetric Encryption Keys
Symmetric encryption is like a single key that both people use to lock and unlock messages. It’s fast and efficient, making it good for protecting a lot of data quickly. The challenge is making sure everyone who needs the key gets it safely and that nobody else intercepts it.
Asymmetric Encryption Keys
Asymmetric encryption works differently. Instead of one key, two keys work together: a public key and a private key. One key locks the message, and only the other can unlock it. This solves the problem of safely sharing keys because the public key can be shared openly while the private key is kept secret. It takes more computer power than symmetric encryption, but makes secure communication between strangers possible. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is one well-known example of this kind. Systems like SSH authorized keys use this form of encryption to provide secure access control.
Overall, symmetric keys excel at speed and efficiency, while asymmetric keys are better at securely sharing encryption capabilities when people don’t know each other yet.
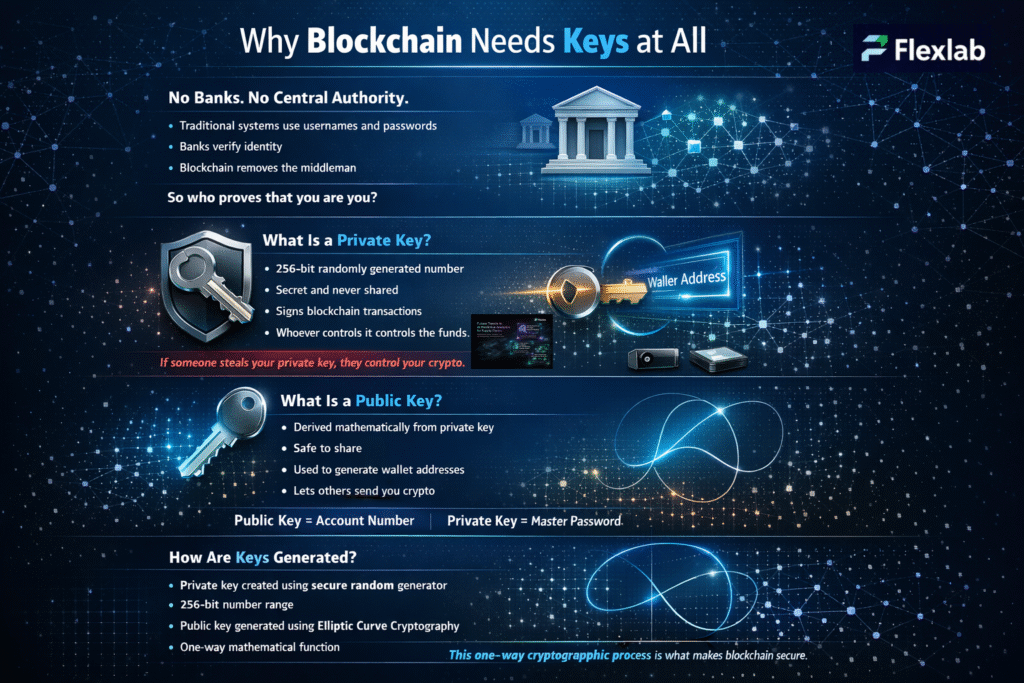
What is a Private Key?
A private key is a secret code used in cryptography that only the owner knows and keeps safe. It works with a public key infrastructure in asymmetric encryption. Anyone can use the public key to encrypt a message, but only the private key can decrypt it, keeping the information secure.
Private keys are also used to create digital certificates and digital signatures, which prove that a message or document really comes from the owner. Software usually generates these keys automatically, and you should never share the private key because anyone who has it can access the encrypted data or impersonate the owner.
In simple terms, think of the private key as a super-secret password that you keep hidden, while the public key is like an open mailbox anyone can put mail into, but only you can open with your secret key. This system allows secure communication even between people who don’t know each other beforehand.
What is a Public Key?
A public key is one part of a pair of cryptographic keys used in public-key (or asymmetric) cryptography. Unlike a private key, the public key cryptography can be freely shared with anyone. It is used to lock or encrypt data so that only the matching private key can unlock or decrypt it.
You use public keys to send messages securely or verify digital signatures. For example, to send a secure message, you encrypt it with the recipient’s public key, and only they can decrypt it with their private key. Public keys solve the problem of sharing encryption keys safely because you don’t need to keep them secret.
This system makes secure communication possible even between strangers, and it’s the foundation for many internet security protocols like SSL/TLS, which keep websites safe when you browse online. In simple terms, the public key is like an open lock anyone can use to secure a message, but only the person with the private key has the key to open it.
Public and Private Key Example
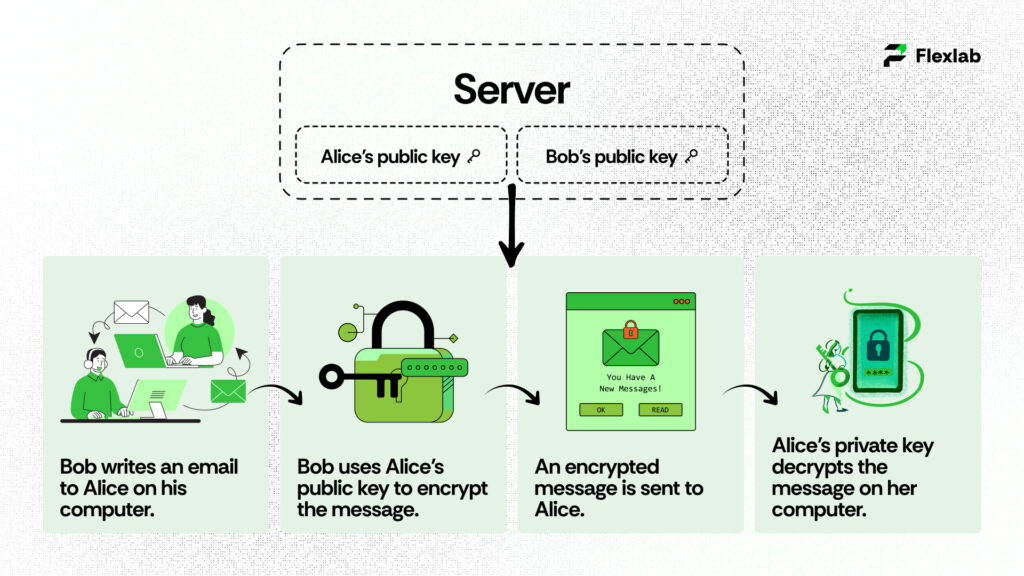
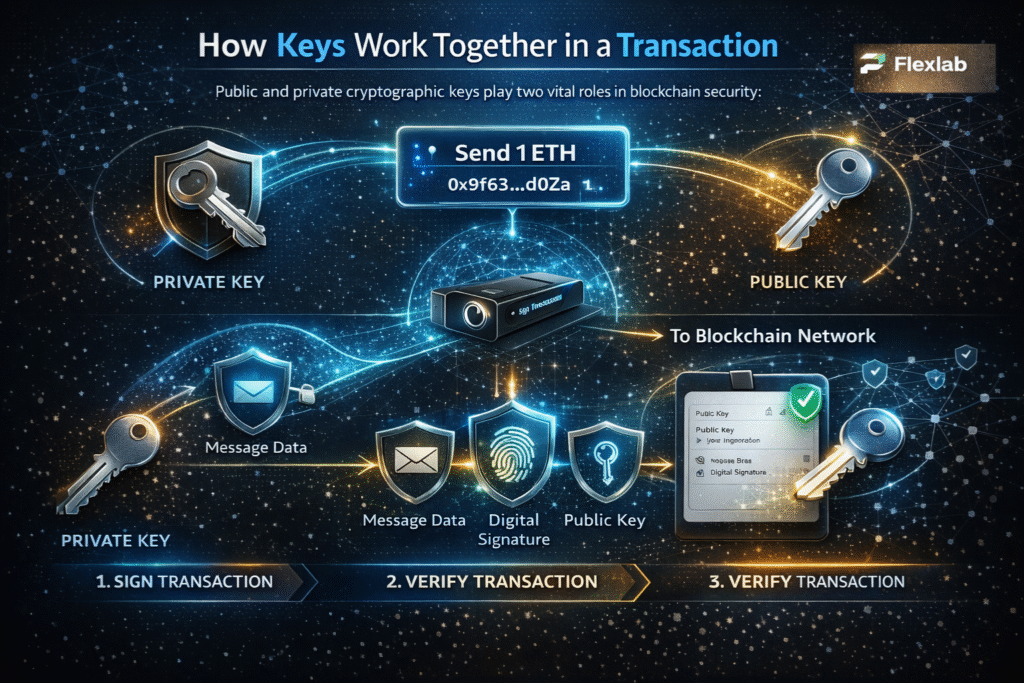
Let’s take two entities, Alice and Bob, and let you explain how public and private keys work together.
Bob wants to send an encrypted email to Alice. For this, he takes Alice’s public key and encrypts his message to her. When Alice receives the message, she uses the matching private key to decrypt Bob’s message.
Attackers might try to compromise the server to access the encrypted information. However, they will be unable to do so because they do not have the private keys to decrypt the message. Alice is the only person who carries the private key. Therefore, Alice is the only one to decrypt and access the message. Whenever Alice wants to reply to Bob’s message, she simply repeats the process.
Uses of Public and Private Key Encryption
| Use Category | Public Key Encryption | Private Key Encryption |
| Key Usage | Uses a pair of keys: one public (shared openly), one private (kept secret) | Uses a single secret key known to both parties |
| Encryption & Decryption | Public key encrypts, private key decrypts | The same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting |
| Main Use Cases | Secure key exchange, digital signatures, email encryption, SSL/TLS for websites | Fast encryption of large data, VPNs, and disk encryption |
| Strengths | Solves key sharing safely, supports identity verification via digital signatures | Efficient and fast for bulk data encryption |
| Weaknesses | Slower and requires more computing power | Key distribution and management are a challenge |
| Examples | RSA, ECC, Diffie-Hellman key exchange | AES, DES |
1. Digital Signatures
A public key can sometimes be used to decrypt a private key. Here comes the creation of digital signatures that assure the person sending the message is who they claim to be.
Generally, the recipient’s public key is used to encrypt the data, and the recipient employs their private key to decrypt it. However, there is no other way to verify the authenticity of the message. Mike could access Alice’s public key because it’s public and send an end-to-end encryption message to Alice while pretending to be Bob. These are considered to be man-in-the-middle attacks.
If Alice uses a digital signature system, she will only trust a message if it has a special signature that proves it really came from the sender. So, Alice will check for Bob’s digital signature on the message. If the message lacks Bob’s digital signature, Alice will proceed cautiously because someone else, like Mike, could be pretending to be Bob.
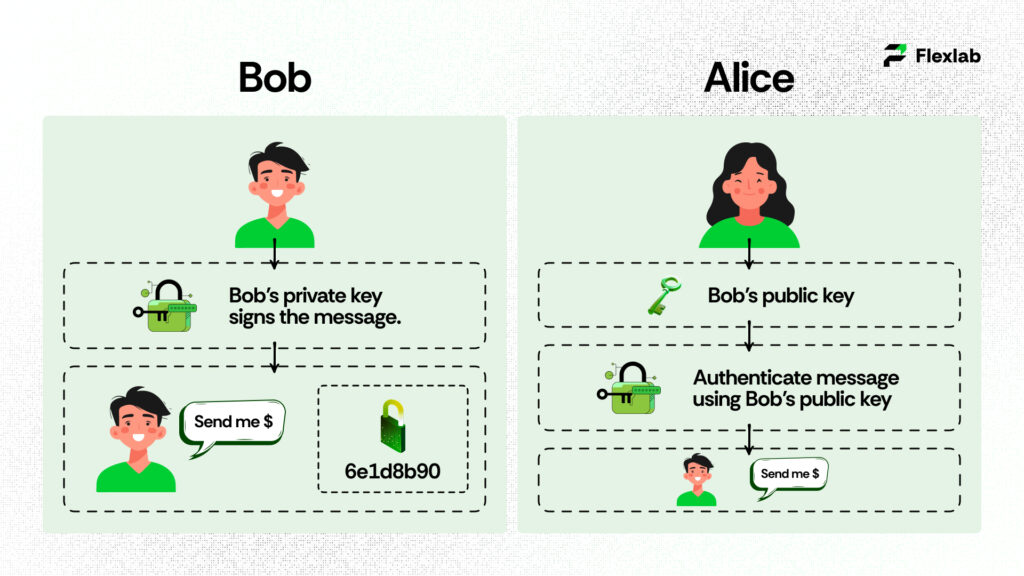
Thus, Bob needs to create a digital signature by signing in to his email account with his private key. Once Alice receives the message from Bob, she can verify the digital signature by using his public key. If the digital signature matches Bob’s public key, since Bob is the only one who created it, then Alice can proceed with confidence that the sender is only Bob, not a middleman or attacker.
2. Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
The Diffie-Hellman key exchange shows how people can safely exchange cryptographic keys even when communicating over a public or open channel.
Before, to send encrypted messages securely, people had to share keys through safe methods, like handing over paper lists of keys through someone they trusted.
The Diffie-Hellman key exchange method allows two people who don’t know each other to create a secret key together, even if they’re using an insecure connection. They both end up with the same secret key, which they can then use to lock their messages so others can’t read them. In a nutshell, the Diffie-Hellman key exchange allows two parties to use symmetric cryptography to encrypt and decrypt the message.
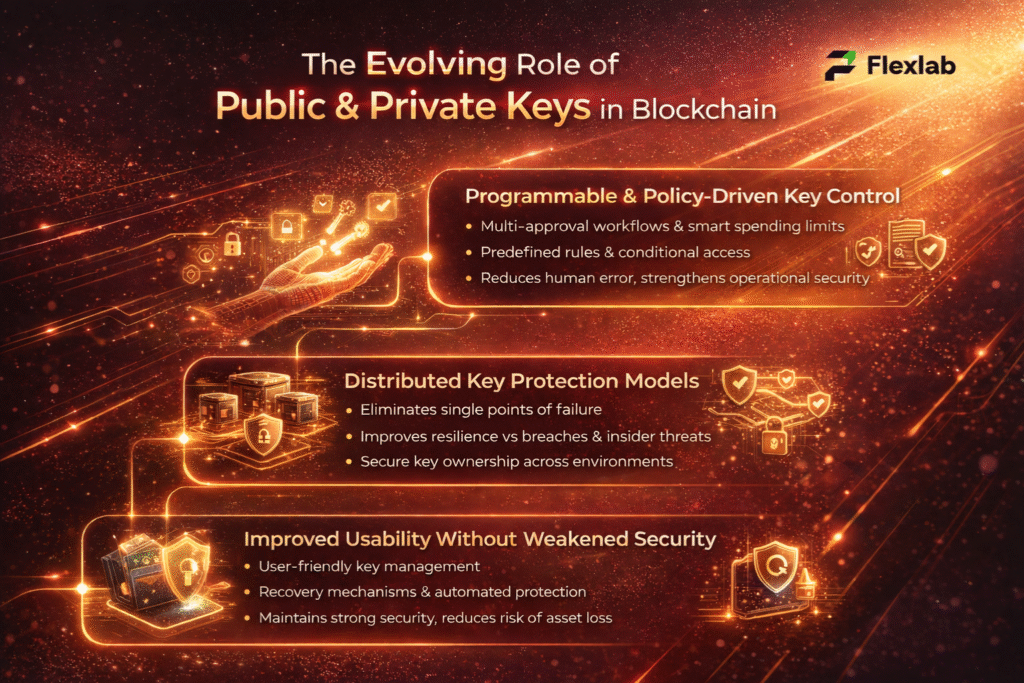
Flexlab has completed numerous projects embedding both public and private key cryptography, significantly enhancing digital security for clients. Their implementations include secure key management and encryption protocols that safeguard communications and data integrity. By integrating robust cryptographic solutions like the Diffie-Hellman key exchange, Flexlab ensures encrypted interactions even over unsecured channels.
Ready to strengthen your digital security?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email us: info@flexlab.io
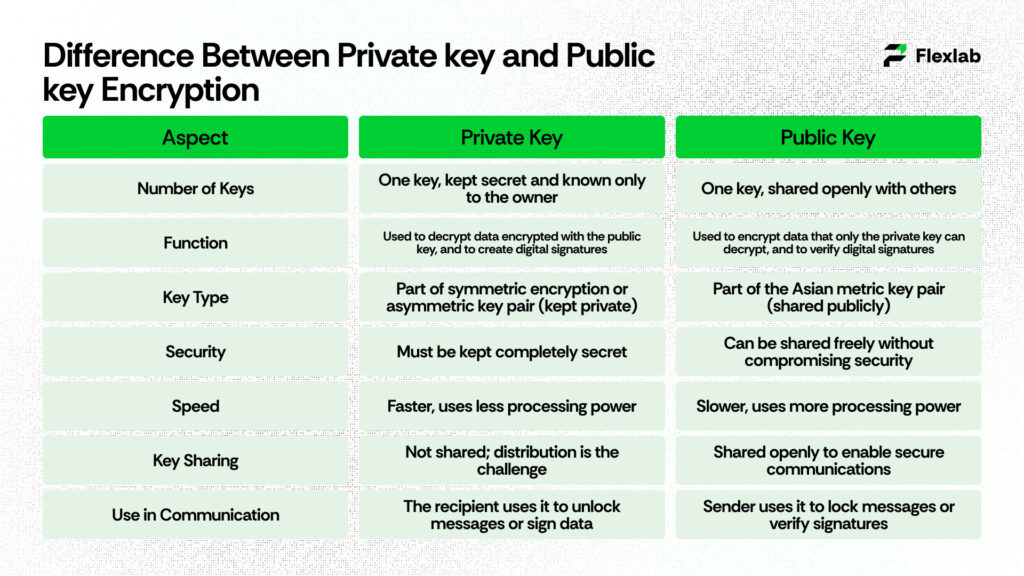
Difference Between Private key and Public key Encryption
Here is the breakdown between public keys and private keys.
-
Visibility and Access
Private keys should be kept confidential and should never be revealed to any third party. They require
- Secure storage
- Makeup procedures
- Strict access controls
On the other hand, you can distribute public keys easily and share them openly through directories, websites, or direct communication without compromising security.
-
Encryption and Decryption Roles
The encryption and decryption roles of these keys are opposite but complementary. Anyone can use your public key to encrypt a message meant for you, but only your private key can decrypt it. This ensures confidentiality even when communicating with strangers because you never share your private key. This asymmetric process is crucial for secure communications over untrusted networks such as the Internet.
-
Authentication Use Cases
You use private keys to create digital signatures—unique codes attached to documents or messages that prove their origin and integrity. Since you alone hold your private key, anyone who verifies the signature with your public key can trust that you sent the message and that it remains unaltered. It works like a digital version of a handwritten signature or a wax seal on a letter.
-
Key Management and Security
Managing private keys is the most sensitive task in cryptography. Losing your private key means losing access to encrypted data or accounts, and unauthorized access can lead to identity theft or data breaches. As a result, private keys are often stored in Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) or encrypted vaults. Public keys don’t require these strict measures, avoiding additional administrative overhead.
-
Role in Asymmetric Encryption
Private keys are the heart of asymmetric encryption, enabling decryption and digital signing, which proves identity. Public keys are the enablers that allow anyone to send encrypted data or verify signatures without compromising security, facilitating safe, one-to-many communications.
-
Speed and Performance
Operations involving private keys tend to be faster because they use less complex mathematical processes compared to public key operations. This speed difference matters when you decrypt many messages or generate many signatures quickly. Public key operations require more computational resources but offer security and flexibility that symmetric systems cannot.
-
Scalability in Networks
One private and one public key per user is enough, regardless of how many correspondents they communicate with. This linear scalability is vital for internet-scale security solutions, avoiding the cumbersome key exchange problems of symmetric encryption and keeping secure communications manageable in large organizations.
Public Key vs Private Key: A Brief Table
Advantages of Public and Private Keys
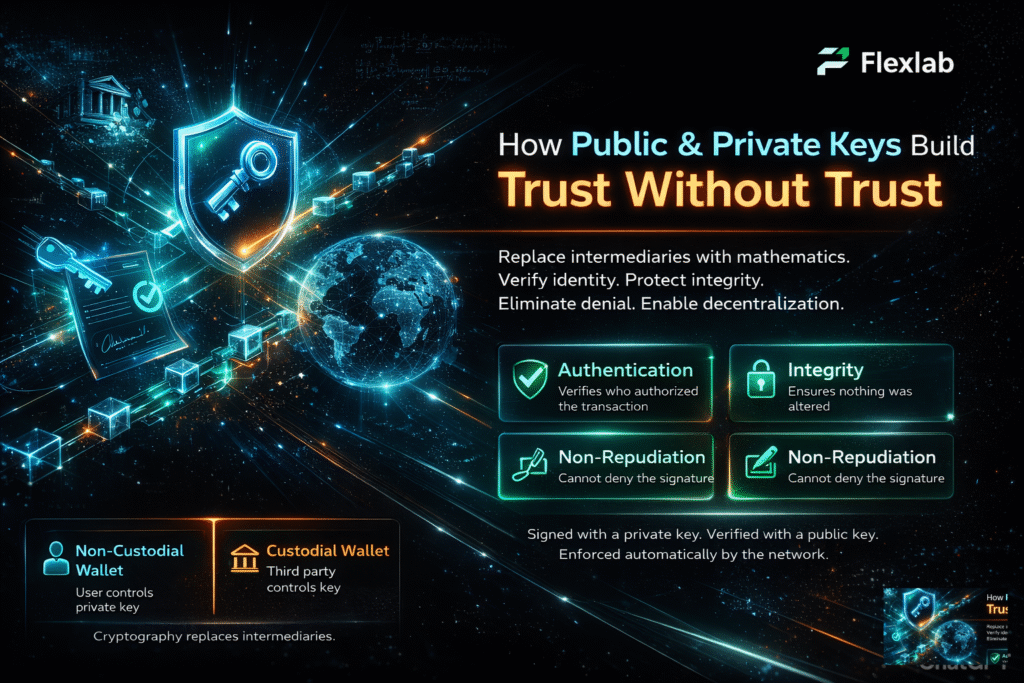
Cryptography public key and private key each have unique advantages that make them essential in modern cryptography. Public key encryption allows secure communication without needing to share a secret key beforehand, making it highly scalable and suitable for large networks.
It provides strong security benefits like confidentiality, authenticity through digital signatures, and non-repudiation, meaning the sender cannot deny sending a message. Sharing the public key openly simplifies key distribution and lets people communicate securely with encryption, even if they don’t know each other. However, it requires more computational power and is slower than private key encryption.
Private key encryption, on the other hand, is much faster and uses less computing power, making it ideal for encrypting large amounts of data quickly. It excels in efficiency and speed for tasks such as bulk data encryption, real-time applications, and devices with limited processing capabilities.
The main challenge with private keys is securely sharing the secret key between parties. These two types of keys often work together: you use public keys to exchange private keys securely and private keys to encrypt the actual data quickly and efficiently. This combination offers both security and performance advantages
Limitations of Public and Private Keys
Here are some limitations of public and private keys. Let’s have a glance at them.
Limitations of Public Key Encryption
- Slower Performance: Public key encryption takes more computing power and time compared to private key methods. This makes it less ideal for encrypting large files or when speed is critical, like real-time communications.
- Complex Setup: It involves many steps, like generating key pairs, managing certificates, and verifying keys. This setup can become complicated, and users may make errors if they don’t handle it carefully.
- Key Security Risks: If the private key gets stolen or leaked, all messages encrypted with the matching public key are at risk. Protecting private keys requires strong security measures.
- Vulnerable to Future Threats: Emerging technologies like quantum computers could crack current public key algorithms, pushing the need for new quantum-safe encryption methods.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Without proper authentication, attackers can intercept and impersonate parties, potentially gaining access to keys and data.
Limitations of Private Key Encryption
- Key Sharing Challenges: Both sender and receiver need the same secret key. Sharing this key safely before communicating is tricky and risky. If the key is intercepted, security is lost.
- Poor Scalability: As the number of participants grows, managing unique secret keys for everyone becomes complicated and hard to maintain.
- No Identity Verification: Private key encryption cannot confirm the sender because both sides use the same key, and it does not support digital signatures.
- Vulnerable to Key Loss: Losing the secret key means permanently losing access to all encrypted data using that key.
- Risk of Brute-Force Attacks: As computing power advances, attackers can eventually guess or crack secret keys unless you use long, complex keys.
How Flexlab Helps You Manage Digital Security

Flexlab is the leading AI and blockchain application development company that helps protect your digital world by securely managing public and private keys through comprehensive key management. It keeps your information safe and secure and verifies your online identity.
We protect your private keys with top-level security and strict access controls, and we share your public keys seamlessly to support secure communication. Flexlab’s solutions easily fit into your existing systems, providing monitoring, regulatory compliance, and expert support to stay ahead of cyber threats.
Ready to boost your security? Contact us today. Explore more about our services and insights by visiting our LinkedIn page and reading our latest updates on our blog. Protect your data with confidence, powered by Flexlab.
Conclusion
Public and private keys form the cornerstone of modern digital security, enabling safe, encrypted communication and trusted identity verification. By using a public key to lock messages and a private key to unlock them, this cryptographic duo ensures that only intended recipients can access sensitive information and confidently verify who sent it.
With increasing adoption driven by growing cybersecurity concerns, these keys safeguard everything from emails and VPNs to blockchain transactions.
Explore More:
- Blockchain Trends Reshaping the Digital Economy in 2025
- Upgrade Your Digital Transformation Strategy with AI and Blockchain
- Is Blockchain Database Right for Your Business? A Comprehensive Guide
FAQs
Q1: Can a public key be used to decrypt?
You cannot use a public key to decrypt data; you use it to encrypt data or verify signatures. Only the matching private key can decrypt data encrypted with the public key.
Q2: How to decode a private key?
To decode a private key, you can use tools like OpenSSL with commands such as openssl rsa -in privatekey.pem -text -noout, which reveals the components of the private key.
Q3: How to decrypt a file with a public key?
You use a private key to decrypt a file because the public key only encrypts it. Cryptography systems do not allow decryption with a public key, and this method is not part of standard encryption practices.
























One Response