Why Quality Assurance Is Essential for Product Excellence
AI Strategy | AI Marketing Tools | Generative AI
In a digital economy where a single software glitch can wipe out $300 million in market value in minutes, understanding quality assurance is a survival requirement. According to recent industry reports, the cost of poor software quality in the US alone has soared to over $2 trillion annually. This staggering figure depicts why quality assurance has evolved from a final bug check into a strategic powerhouse driving the entire SDLC.
A modern quality assurance process focuses on defect prevention through rigorous quality assurance standards and proactive planning, rather than reacting to errors after a product reaches the user. When QA is neglected, the consequences are catastrophic, including broken application programming interface connections, security breaches, and frustrated users abandoning your product.
To stay competitive, industry leaders are embedding TQM principles into every phase of product development, from the first line of code to the moment AI agents improve customer experience in a live environment. In this blog, we’ll explore the critical role of quality assurance, compare it with quality control, and show how each impacts product reliability and business success.
What Is Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance is a structured, proactive approach to ensuring that a product or service consistently meets defined requirements before it reaches the users. Rather than reacting to defects after launch, QA focuses on improving the systems, workflows, and standards used during product development, thereby preventing issues earlier.
Essentially, QA is about reliability and trust. It ensures teams follow repeatable processes, document expectations clearly, and validate outcomes at every stage. Modern QA integrates seamlessly throughout the build process, supporting faster releases while maintaining stability. If implemented correctly, it becomes a business enabler, helping teams scale without sacrificing quality.
-
Why Quality Assurance Is Important
Quality assurance is important because it protects brand reputation, prevents costly errors, and ensures a reliable experience for customers. By following a structured quality assurance process, you can streamline product development, reduce defects, and maintain compliance with industry standards. In today’s fast-paced digital world, strong QA practices are mandatory to deliver secure, functional, and high-quality products that meet both business and customer expectations.
What Is the Difference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control?
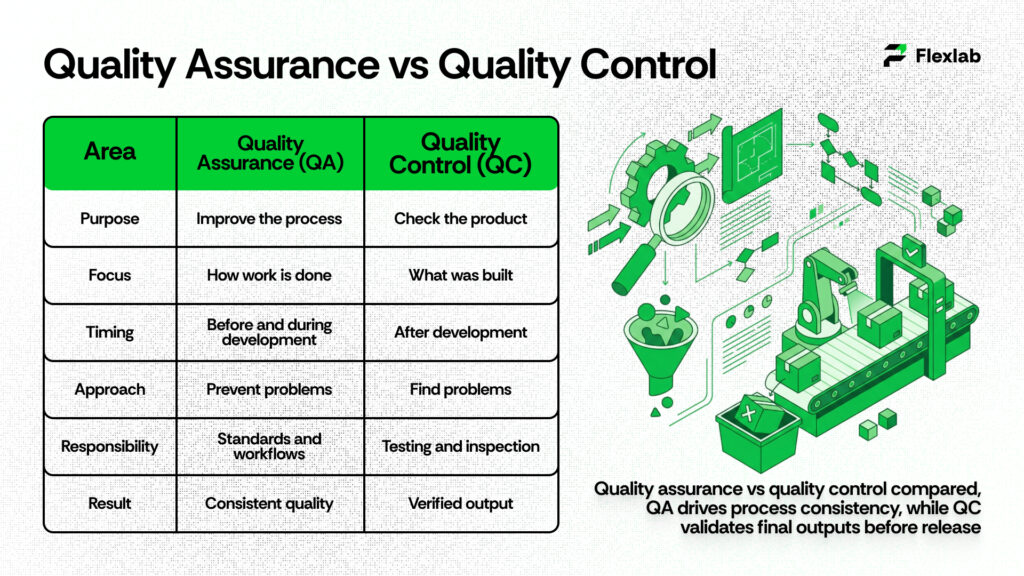
Understanding quality assurance vs quality control enables teams to build better products and avoid costly mistakes. While both aim to improve quality, they focus on different stages of the development process and serve different roles.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a proactive, process-focused practice designed to prevent defects before they occur. In particular, it concentrates on how work is planned, documented, and executed throughout product development. Moreover, QA establishes standards, defines workflows, and ensures teams follow consistent methods. As a result, organizations can deliver reliable, high-quality results consistently.
Quality Control
Quality control is a reactive, product-focused practice that identifies defects after development is complete. It involves testing, inspections, and reviews to confirm that the final product meets defined requirements. QC validates outcomes, ensuring issues are detected before release.
The Role of Total Quality Management in Quality Assurance
Total quality management is a company-wide approach that ensures quality is built into every function, rather than being treated as a final checkpoint. Instead of isolating responsibility within a single team, TQM aligns leadership, operations, and support functions around a shared commitment to consistency and customer satisfaction.
In quality assurance, TQM provides the strategic foundation that connects people, processes, and accountability. It encourages prevention over correction, long-term improvement over short-term fixes, and data-driven decisions over assumptions. When applied correctly, TQM strengthens trust across teams and supports sustainable growth without slowing innovation.
By embedding quality into organizational culture, total quality management allows QA practices to scale effectively while maintaining reliability and clarity across the business.
The 7 Pillars of Quality Assurance
Strong quality outcomes are built on foundational principles that guide how organizations operate, make decisions, and maintain high standards. These principles form the foundation of effective quality management, enabling teams to deliver consistent and reliable results.
Here are the seven pillars that every successful quality assurance program relies on:
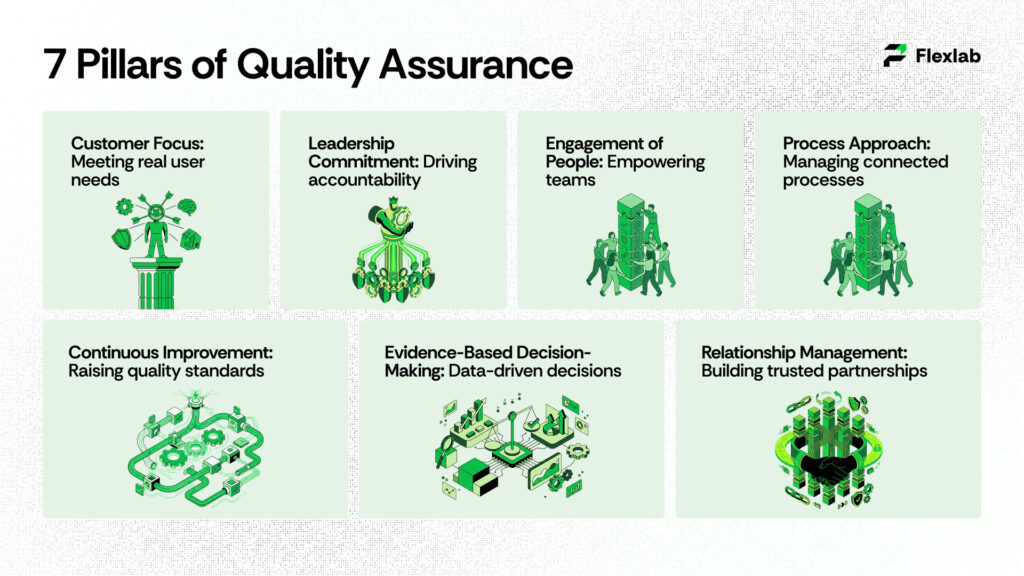
1. Customer Focus
Quality is measured by how well a product meets real-user requirements, not just internal expectations. Delivering value and usability is the ultimate goal.
2. Leadership Commitment
Leaders must set clear expectations, provide resources, and develop accountability to maintain standards across teams.
3. Engagement of People
Every team member, from developers to support staff, should feel empowered to identify risks and contribute to quality improvement.
4. Process Approach
Work should be managed as connected processes rather than isolated tasks, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and better coordination across departments.
5. Continuous Improvement
Through regular evaluation and refinement, organizations can adapt, learn from mistakes, and therefore continuously raise quality standards.
6. Evidence-Based Decision-Making
Decisions about quality should be guided by data and metrics, which ensure reliable and predictable outcomes.
7. Relationship Management
Strong standards for suppliers and partners prevent external risks from affecting the quality of the final product, building trusted relationships that support overall success.
Quality Assurance Standards & ISO 9000
Quality assurance standards are a global language of trust. For any business looking to establish credibility, complying with frameworks such as ISO 9000 is the ultimate seal of approval.

How Standards Boost Credibility:
- Global Recognition: ISO certification signals to international clients that your quality assurance process meets systematic, globally recognized benchmarks.
- Risk Mitigation: These standards require organizations to identify and manage risks systematically, ensuring product development stays on track and potential failures are detected early.
- Operational Efficiency: Established quality assurance standards reduce waste and unnecessary repetition. Whether using statistical process control to monitor manufacturing or automated testing for software, teams know exactly what quality should be.
- Customer Confidence: Following quality assurance best practices verified by third-party standards builds brand loyalty further than what marketing alone can achieve.
By integrating these standards into your software quality assurance strategy, you can easily create a culture of excellence reflected in every application programming interface and every interaction where AI agents enhance customer experience.
Types of QA Testing
A resilient quality assurance process relies on multiple testing methods to ensure a product’s reliability in every scenario. Utilizing various types of QA testing strengthens credibility, minimizes risks, and supports a successful software development life cycle.
-
Functional Testing
Functional testing ensures that each feature works as targeted, based on business requirements. For instance, if you click Add to Cart, does the item appear correctly? This ensures product development goals are met on a foundational level.
-
Regression & Automated Testing
As new code is added, regression testing identifies any unintended issues, while automation helps execute repetitive tests quickly and accurately. Consequently, this combination saves time and reduces human error, thereby keeping the product stable with each update.
-
API & Integration Testing
Modern software relies on an application programming interface to communicate with other services. QA teams test these connections to ensure data flows correctly, maintaining a seamless user experience.
-
Performance & Load Testing
Additionally, performance testing simulates high traffic to measure speed, responsiveness, and stability. This step is crucial for quality management, ensuring products remain reliable under heavy usage.
-
Security Testing
Security testing identifies security gaps and protects user data. It is a core quality assurance best practice to safeguard the system and maintain overall product transparency.
-
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
Finally, real users test the product to ensure it is insightful and meets their needs. UAT confirms that a product is not only functional but also user-friendly and ready for launch.
-
Why Diversity in Testing Matters
Furthermore, using multiple types of QA testing ensures total quality across all aspects of the product. Focusing on only one area might leave critical security, performance, or integration issues undetected. By covering all these bases, QA teams provide a safety net that allows developers to innovate with confidence.
Automation Tools: The Modern QA Engine

In a fast-moving product development cycle, manual effort alone can’t keep up. Automation tools are the secret ingredient that lets teams scale efficiently, improving speed without sacrificing quality. By integrating these into your software development life cycle, you can choose from reactive bug-fixing to proactive quality management.
Essential Quality Assurance Tools for 2026
Selecting the right tech stack is half the battle. Key tools dominating the industry include:
Selenium & Playwright: Industry leaders for web-based automated testing, providing strong cross-browser support.
Appium: Handles native and hybrid mobile apps efficiently, supporting modern product development.
Postman: Critical for testing your application programming interface (API) to ensure smooth data exchange.
JMeter: Simulates thousands of users for performance testing, ensuring platform stability.
Why Automated Testing is Critical
Automation creates a safety net. By following quality assurance best practices such as continuous testing, every code commit is automatically verified. This reduces human error, speeds up regression testing, and allows testers to focus on high-value exploratory work. Moreover, integrating AI-driven tools can further improve customer experience, making QA smarter and more proactive.
Quality Assurance Process
The quality assurance process is the structured framework that ensures products meet high standards before they reach customers. Unlike reactive quality checks, QA focuses on prevention over correction, embedding quality into every stage of product development. A typical quality assurance process follows the following key steps:
1. Requirement Analysis
Understanding business and user requirements is critical. In this step, everyone becomes aware of what quality looks like for the products, thereby setting measurable standards.
2. Test Planning
Test plans outline the scope, objectives, resources, and schedule for QA activities. By doing so, they help teams align their work with the quality assurance standards, ensuring that nothing is overlooked.
3. Process Implementation
During development, QA practices like code reviews, checklists, and peer audits are applied to prevent errors early. Embedding these practices reduces rework and improves efficiency.
4. Testing & Validation
This stage involves executing test cases, performing inspections, and, wherever possible, using techniques such as automated testing. The goal is to identify defects before the product reaches the end user.
5. Reporting & Feedback
QA teams document findings and provide actionable feedback to developers and stakeholders. As a result, lessons are captured, and continuous improvement can be applied in future cycles.
6. Continuous Improvement
By analyzing metrics, monitoring performance, and implementing refinements, the QA process evolves. This step closes the loop and strengthens reliability across future SDLC versions.
Quality Assurance Examples: Real-World Impact Across Industries
Quality Assurance is really about peace of mind. It identifies small issues before they turn into big, expensive problems and keeps systems reliable. It protects both customers and the business. The following examples show how an early QA catch in finance can save millions and a lot of headaches.
1. The Financial Sector: Preventing The Million Dollar Glitch
In Fintech, an error in an application programming interface (API) can lead to financial disaster. Imagine a banking app where a currency conversion error occurs due to a lack of statistical process control.
- The Scenario: A major global bank is updating its cross-border payment system.
- The QA Strategy: They implement thorough automated testing to verify millions of transaction variations. Because security is paramount, they utilized various types of QA testing, such as penetration testing, to ensure hacker-proof code.
- The Result: By following strict quality assurance standards, the bank identifies a logical error in the application programming interface that would have double-charged users. The bug is fixed in the software development life cycle (SDLC) before a single dollar is moved.
2. Healthcare Technology: When Quality Saves Lives
Software quality assurance is literally a matter of life and death in healthcare. Medical devices and patient tracking systems must be flawless.
- The Scenario: A health-tech startup is developing an AI-powered diagnostic tool.
- The QA Strategy: They use total quality management to ensure every department, from data science to UI design, is aligned. They deploy AI agents to improve customer experience by simulating how doctors interact with the data under high-stress emergency room conditions.
- The Result: Through extensive user acceptance testing (UAT) and quality management protocols, they ensure the software integrates perfectly with hospital databases. The product launches with zero critical defects, gaining FDA approval faster than expected.
3. E-commerce: Handling the Black Friday Surge
The cost of quality, for retailers, is never more apparent than during peak shopping seasons.
- The Scenario: A national retailer expects 10x their normal traffic on Black Friday.
- The QA Strategy: They use automation tools such as JMeter to perform massive load testing (one of the essential types of QA testing). They also use statistical process control to monitor server response times in real-time.
- The Result: The quality assurance process reveals that the checkout application programming interface bottlenecks when more than 50,000 users are active. The team scales their cloud infrastructure and optimizes the code weeks before the event, resulting in their most profitable and crash-free holiday season ever.
How to Choose the Right Quality Assurance Tools for Your Business
With so many automation tools and quality assurance services in the market, how do you pick the right ones? It’s not about buying the most expensive software; it’s about alignment with your product development goals.
Assessing Your Needs
- Project Scale: If you’re a small startup, you might start with open-source quality assurance tools such as Selenium. If you’re an enterprise, you might need a full-suite quality management platform.
- Team Expertise: Does your team have the coding skills for script-based automated testing, or do you require low-code automation tools?
- Budget vs. Risk: In high-risk industries (like Finance or Healthcare), investing in premium quality assurance services is an insurance policy against future litigation and loss.
Flexlab Software Quality Assurance That Prevents Problems Before Launch

Flexlab empowers teams to ship rock-solid software without last-minute disruptions by embedding quality assurance into every stage of development. We detect risks early, fortify your SDLC, and ensure performance, security, and integrations hold up under pressure. If you’re ready to replace firefighting with predictable, high-quality releases, the next step is a conversation.
Ready to Grow Your Business?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email us: info@flexlab.io
Explore our services to see how we leverage AI Assistants, automation, and modern engineering practices to solve critical business challenges, or check out our portfolio to see real automation and AI-driven QA solutions built for speed, scale, and reliability. To discuss a strategy tailored to your goals, contact us and start a conversation today. Dive into practical insights on the blog page to stay ahead of trends, or follow our latest thinking and updates on LinkedIn.
- Smart Contract Development: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
- How to Choose the Right AI Automation Agency For Your Business?
- Upgrade Your Digital Transformation Strategy with AI and Blockchain
Conclusion: Quality Assurance Is Not an Act, It’s a Habit
Quality Assurance is about trust. It’s the commitment you make to customers that your product will work when it matters most. From the earliest stages of the software development life cycle to the moment AI agents enhance customer experiences in production, quality should be the heartbeat of your organization.
By strengthening your quality assurance process, understanding the difference between quality assurance vs. quality control, and embracing automated testing, you’re doing more than preventing bugs; you’re building a reliable brand. And when you’re ready to scale with confidence, investing in professional quality assurance services can help ensure your next launch isn’t just functional, but exceptional.
FAQs
- How can AI improve software quality assurance?
AI enhances QA by automating repetitive testing, detecting patterns in defects, and predicting potential vulnerabilities before they occur. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets, prioritize test cases, and simulate real-world user interactions. By integrating AI into QA workflows, teams can achieve faster testing cycles, higher accuracy, and a smarter, proactive approach to preventing errors.
- What role do metrics and KPIs play in effective QA?
Metrics and KPIs provide measurable insight into the effectiveness of QA processes. Tracking defect density, test coverage, and time-to-resolution helps teams identify weaknesses, optimize testing strategies, and make data-driven decisions. Using these metrics ensures accountability, improves transparency, and drives continuous improvement across software development projects.
- What are common pitfalls businesses face when implementing QA, and how can they be avoided?
Businesses often struggle with QA when testing is done too late, processes are inconsistent, or tools are underutilized. Other pitfalls include poor documentation, unclear requirements, and neglecting automated testing. These issues can be avoided by embedding QA early in the SDLC, using automation strategically, establishing clear standards, and fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.