Public vs Private Blockchain: Finding the Right Fit for Your Enterprise
Blockchain App Development | Smart Contracts | Blockchain and IoT
Trust is the new currency for digital businesses. With public vs private blockchain solutions, companies can share and protect data with full confidence, transparency, and security. It is built for the upcoming digital future. Understanding the difference between public and private blockchains can help you select the right track for your business growth.
One major question that divides today’s innovators and executives alike is whether your business should build on the open transparency of a public blockchain or rely on the controlled environment of a private blockchain. The difference goes far beyond technical design; it shapes how your organization operates, secures data, and earns customer confidence.
In this blog, we’ll discover how both blockchain models work, explore their advantages and challenges, and reveal which is better suited for your specific business goals. At the end of this blog, you’ll know how to choose the blockchain foundation that strengthens your organization’s future.
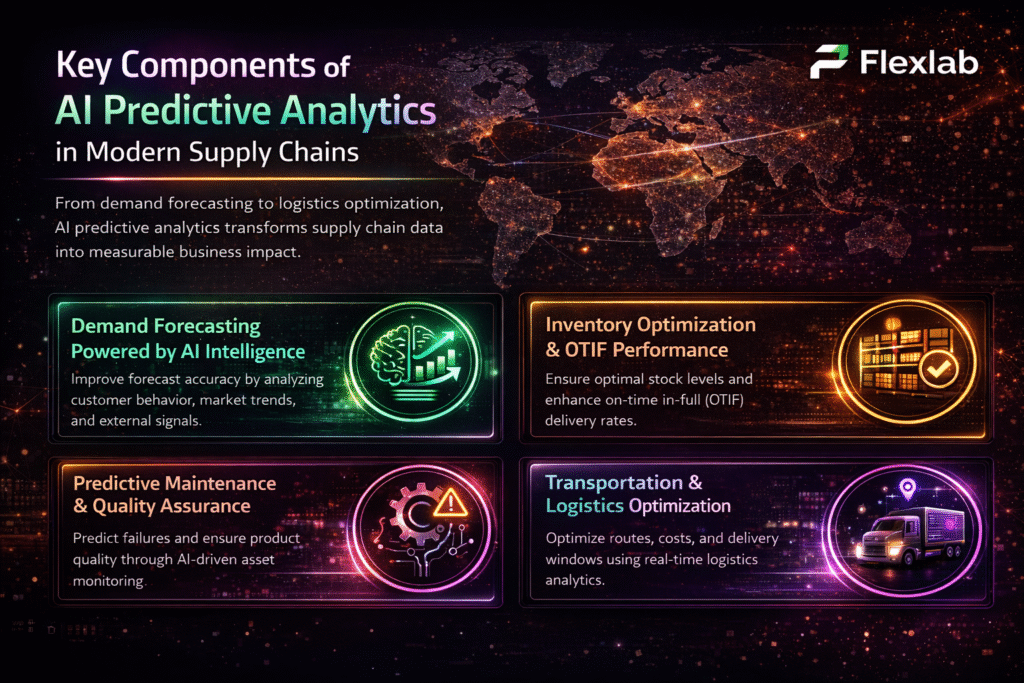
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology
To understand why businesses are turning to blockchain, imagine a digital ledger that records every transaction in real-time, visible to all participants, and it’s impossible to tamper with it. That’s the core of blockchain technology. It is a shared, transparent system designed to remove intermediaries and build trust through automation.

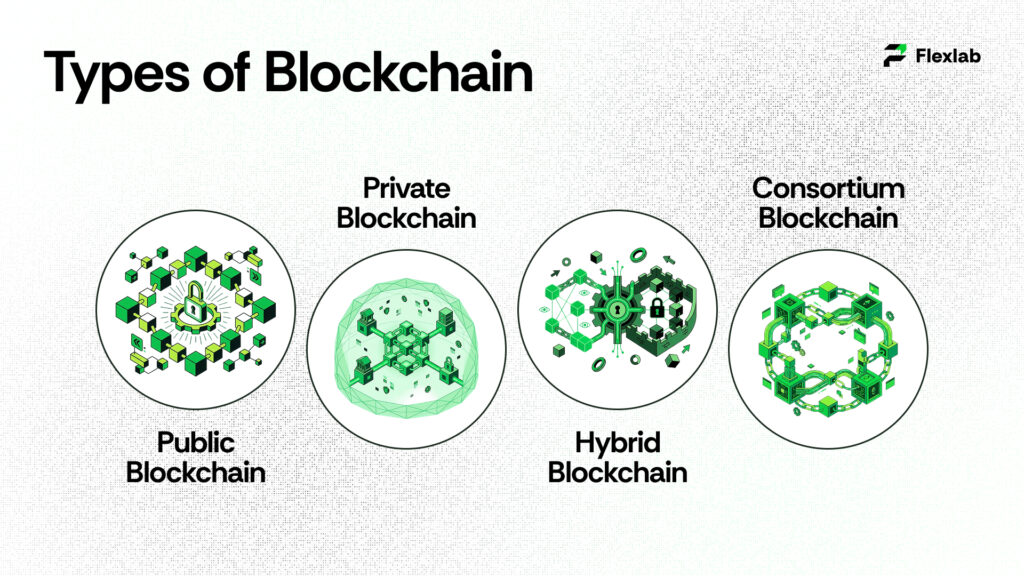
Each block in this chain stores verified data and is linked to the previous one using advanced cryptography techniques. These mathematical safeguards make it nearly impossible to alter the information that has been recorded once. Instead of relying on one central database, blockchain distributes its records across multiple computers, making it secure, transparent, and highly resistant to attacks or errors. There are different types of blockchain models, including public, private, consortium, and hybrid, each tailored to meet specific business needs such as scalability, privacy, and governance.
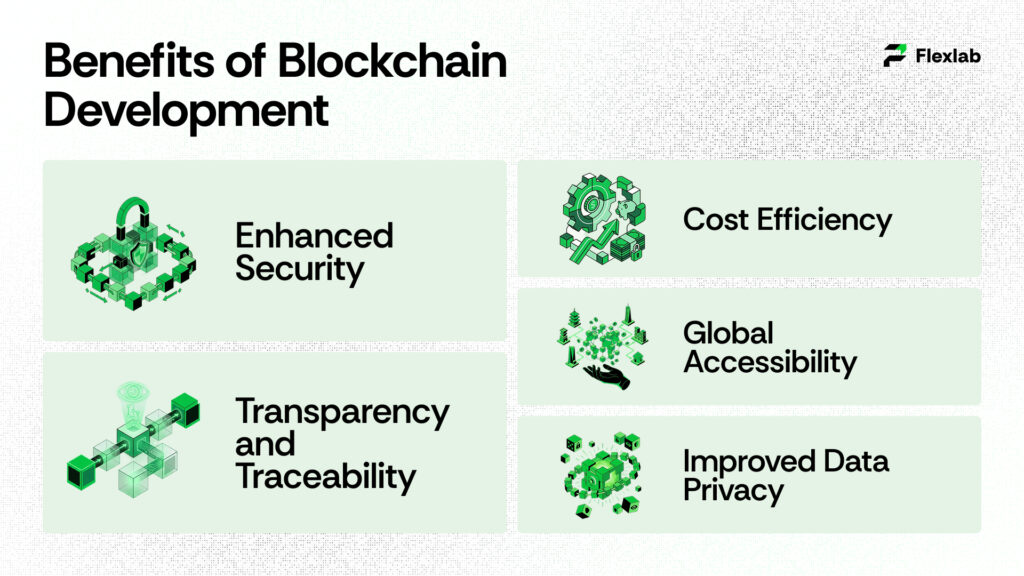
Consequently, this innovation opens doors to new opportunities for companies. From supply chains and healthcare to digital finance, blockchain for business provides faster verification, improved traceability, and stronger accountability. It’s not just about new emerging technology; it’s about redefining how trust works in a digital-first economy.
What is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is a digital network where anyone can participate, validate, and store information independently. It serves as the foundation of decentralized systems like Bitcoin and Ethereum, where transparency replaces trust, and data integrity is maintained collectively by the community instead of a single organization. Let’s explore some key features that make public blockchains truly open and transformative.
-
Open, Transparent, and Decentralized
A public blockchain functions as an open digital ecosystem, where anyone from anywhere in the world can join, verify transactions, and contribute to the network’s growth. There is no central authority involved in controlling it, which makes it one of the purest forms of decentralization. Most common examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum, where users rely on community-driven consensus other than corporate or government control.
-
The Power of Transparency
In a public blockchain, every transaction is recorded on a transparent ledger that anyone can audit, therefore ensuring complete visibility. Because of this openness, digital currencies thrive on public blockchains; in fact, they allow users to exchange value globally without the need for intermediaries or restrictive oversight. However, transparency comes with trade-offs: because everyone can participate, these networks often process fewer transactions per second compared to private systems.
-
Resilience and Security
A primary strength of public blockchain is its network resilience. In any case, if part of the system goes offline or fails, the remaining parts continue to operate seamlessly, ensuring the data remains secure and accessible. This inherent durability makes public blockchains ideal for applications where transparency, community trust, and long-term reliability are essential.
What is a Private Blockchain?
A private Blockchain is a network built for trust, where only permissioned participants can access, verify, and share data securely. It’s the essence of a private blockchain. It follows the same foundational principles of blockchain technology, including immutability, transparency, and security, but within a restricted environment designed for privacy and control. Organizations adopt private Blockchain to automate internal workflows, manage sensitive information, and meet regulatory requirements without exposing data to the public. Let’s break down the fundamental traits that highlight why private blockchains stand out in the digital landscape.
-
Controlled Access and Governance
Only verified members can join and participate in private blockchain networks. This requires that every node or user must authorize before they can participate. This limitation makes it ideal for enterprises that handle confidential and sensitive data, such as finance and logistics. Furthermore, blockchain technology in healthcare relies on private blockchains to ensure compliance and protect patient or customer information.
-
Performance and Efficiency
Private blockchains are optimized for speed and scalability due to the involvement of trusted participants. These systems can process a higher number of transactions per second, ensuring smooth and reliable real-time data processing. This makes them a go-to choice for enterprise blockchain implementations seeking efficiency and consistency.
-
Security and Trust
Advanced cryptography techniques and permission-based access play a vital role in maintaining security in private blockchains. Each transaction is validated and traceable, minimizing risks of tampering or fraud. This built-in accountability allows organizations to maintain both security and trust within their networks.
Public vs Private Blockchain: A Detailed Comparison
Choosing between a public blockchain and a private blockchain isn’t just about technology; it’s about aligning your business goals with the right infrastructure. Both have unique advantages and trade-offs that determine how your organization handles security, speed, and transparency. To help you make an informed decision, let’s compare the two side by side.
1. Accessibility and Participation
A public blockchain is open to everyone. Anyone can read, write, or verify transactions without requiring any approval. This openness encourages innovation and network resilience, but it can slow down the overall performance.
In contrast, a private blockchain requires permission; only verified members can join. This model is best for enterprises that prioritize data protection, compliance, and operational efficiency over full decentralization.
2. Security and Trust
Public blockchain networks rely on consensus-building techniques such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, which use distributed nodes to validate every block. This makes them highly secure and tamper-resistant.
On the other hand, Private blockchains utilize cryptography techniques and controlled access to protect data. Trust is established among authorized participants, making them ideal for blockchain and for business use cases where confidentiality is mandatory.
Both public and private systems utilize different consensus-building techniques, such as Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or Proof of Authority, to ensure that all participants agree on valid transactions while maintaining data integrity.
3. Performance and Speed
Since thousands of nodes must agree before confirming a transaction, public blockchains usually handle fewer transactions per second.
Conversely, private blockchains eliminate this bottleneck by limiting validator access. It enables faster real-time data processing, which is crucial for industries that require immediate results. Private networks also enable efficient real-time data processing, allowing businesses to execute transactions instantly while maintaining control and accuracy.
4. Use Cases
Public blockchains are best for decentralized applications, digital currencies, and platforms that demand transparency.
However, private blockchains excel in internal business processes such as enterprise blockchain systems and blockchain technology in healthcare, where privacy and scalability are essential.
5. Maintenance and Costs
In Public blockchain networks, no single entity bears the cost because it relies on a decentralized worldwide community of users. Many organizations now utilize Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) platforms to build, host, and scale their blockchain solutions without maintaining extensive infrastructure.
By contrast, private blockchains require dedicated blockchain development services. A blockchain network provides a service platform that helps to maintain, set up, and scale. While they may cost more upfront, they often deliver greater control and compliance benefits in the long run.
Public vs Private Blockchain: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
| Accessibility | Open to anyone, no central authority. Anyone can join, verify, or store data. | Access is restricted; only verified or authorized members are allowed to participate. |
| Transparency | Fully transparent, all transactions are visible on the public ledger. | Transactions are private and visible only to permitted participants. |
| Security Model | Utilize decentralized consensus-building techniques like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake for validation. | Relies on permissioned access, internal validation, and advanced cryptography techniques. |
| Performance | Slower due to multiple validators; fewer transactions per second. | High-speed and real-time data processing is necessary due to the limited number of participants. |
| Control | No central authority, governed by the community. | Managed by a single organization or consortium. |
| Scalability | Harder to scale due to public verification. | Easier to scale within private networks and enterprises. |
| Use Cases | Best for digital currencies, decentralized apps (DApps), and public transparency projects. | Ideal for enterprise blockchain, supply chain management, and blockchain technology in healthcare. |
| Cost & Maintenance | Lower maintenance — community-driven, but may require more computational power. | Higher setup cost, maintained via blockchain development services or a blockchain as a service provider. |
| Network Resilience | Extremely resilient, continues operating even if parts of the network fail. | Resilient within its permissioned structure, but it depends on centralized control. |
A public blockchain is perfect for businesses that thrive on openness, collaboration, and global participation.
A private blockchain is ideal for organizations that demand performance, privacy, and control over sensitive data.
Both models reflect the future of blockchain technology, but the best choice depends on your industry goals, compliance needs, and the transparency you are ready to adopt.
Choosing the Right Blockchain for Your Business
Selecting between a public and private blockchain is more than a technical decision; it’s about aligning technology with your business goals. The right choice totally depends on how much transparency, control, and scalability your organization requires.
1. Understand Your Core Objective
If your goal is open collaboration, public participation, or decentralized transactions, a public blockchain like Ethereum or Solana may be best for you. However, if you prioritize privacy, data ownership, and compliance, a private blockchain such as Hyperledger Fabric or Corda could be the better fit for you.
2. Evaluate Governance and Compliance Needs
Industries with strict data protection laws, including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management, often rely on private blockchains for permissioned access, auditable records, and regulatory compliance. In contrast, public blockchains offer global visibility and decentralized governance, but with less direct control over network rules.
3. Consider Future Scalability
Think strategically, will your blockchain need to support growing transactions, cross-border operations, or multi-party integrations?
Private networks deliver speed and customization, while public blockchains enable broader ecosystem participation and interoperability.
Starting with a pilot project by using a private or hybrid blockchain, then expanding to a public network once your model is identified as secure, compliant, and scalable. Collaborating with an experienced blockchain development company can simplify deployment, ensure compliance, and help align the technology with your long-term business strategy. That’s where Flexlab comes in, a leading blockchain development company helping businesses implement secure, scalable blockchain ecosystems tailored to their industry. Next, let’s take a closer look at how businesses across industries are putting these blockchain models to work in the real world.
Real-World Use Cases of Public and Private Blockchains
Understanding how organizations apply public vs private blockchains in practice reveals their true business value and real-world potential to adopt blockchain technology.
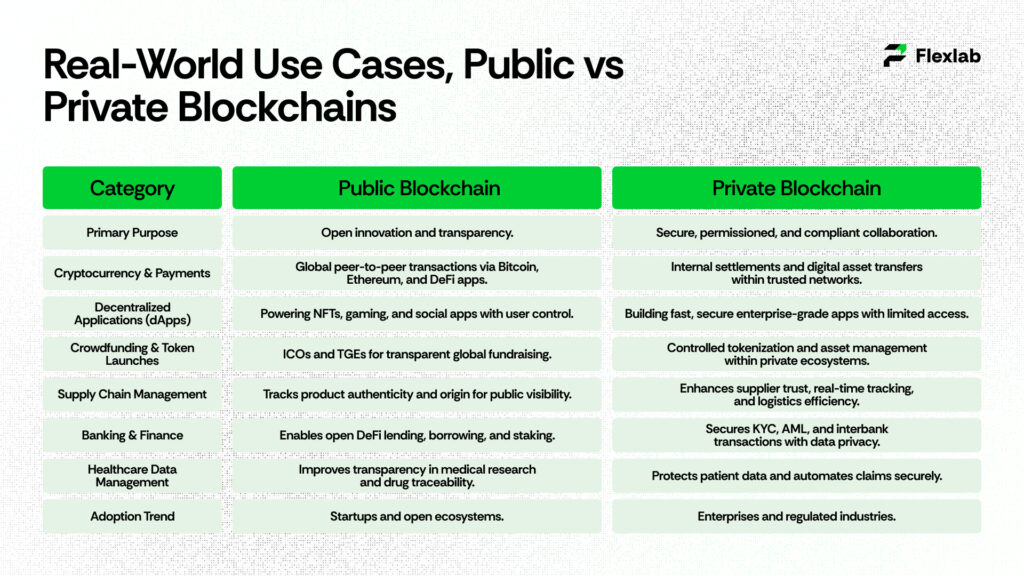
Public Blockchain Use Cases
- Cryptocurrency and Payments
Public blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum enable peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. They’re ideal for global payments, DeFi platforms, and tokenized assets, where transparency and decentralization are crucial. Public blockchains also power secure crypto wallets, enabling users to store, send, and verify digital assets globally without relying on centralized intermediaries. - Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Developers build dApps on public networks to offer open access, trustless operations, and smart contract automation. Examples include NFT marketplaces, gaming platforms, and social apps that empower users to control their data.
- Crowdfunding and Token Launches
Moreover, through Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Token Generation Events (TGEs), startups can leverage public blockchains to raise capital globally while connecting directly with investors, thus cutting out traditional financial barriers.
Private Blockchain Use Cases
- Supply Chain Management
Enterprises such as Walmart and Maersk use private blockchains to track goods, verify authenticity, and improve transparency across suppliers. It builds their trust and efficiency in complex logistics networks. These networks enhance supply chain transparency, allowing real-time tracking, product verification, and trust across suppliers and logistics partners. - Banking and Finance
Financial institutions launch private blockchains for secure interbank transactions, trade settlements, and KYC/AML verification. These systems ensure data privacy and regulatory compliance while reducing transaction costs.
- Healthcare Data Management
Hospitals and medical providers prioritize private blockchains to secure patient records, control data access, and share information safely among trusted parties, ensuring accuracy, security, and confidentiality. Additionally, private blockchains enable automated claims processing, reducing paperwork, minimizing delays, and improving data accuracy across healthcare systems.
Many forward-thinking organizations are adopting hybrid blockchain solutions, amalgamating the transparency of public networks with the control of private systems, offering the perfect balance of trust, speed, and privacy.
The Future of Blockchain for Businesses
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its impact on business transformation is becoming impossible to ignore. The future will not be about choosing between public and private blockchains, but about how effectively and efficiently organizations can integrate and innovate using both.
1. Rise of Hybrid and Consortium Blockchains
The next generation of blockchain adoption is moving forward towards hybrid and consortium models, combining the openness of public systems with the security of private networks. These solutions enable interconnected ecosystems, where multiple companies can collaborate securely while maintaining data privacy and operational control.
2. Interoperability and Cross-Chain Integration
Today, businesses are increasingly demanding cross-chain communication, as it enables different blockchains to share data and assets seamlessly. Consequently, projects focusing on interoperability—such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and Chainlink—are paving the way for a more connected blockchain landscape. As a result, enterprises can operate more efficiently and collaboratively across diverse networks.
3. Blockchain Meets Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The integration of AI and blockchain is reshaping how businesses handle data automation, analytics, and decision-making. Blockchain ensures data integrity and transparency, while AI enhances predictive insights and process optimization, together delivering smart, trustworthy business ecosystems.
4. Greater Focus on Sustainability
As environmental awareness grows, future blockchain solutions will emphasize energy efficiency and green consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA). This advanced shifting ensures that blockchain innovation aligns with global sustainability goals and eco-friendly business practices.
5. Regulatory Maturity and Enterprise Confidence
Governments and regulatory bodies are now developing clear frameworks for blockchain adoption. Providing more confidence to enterprises to increase investment. With standardized compliance, identity verification, and data protection laws evolving, blockchain will become a global mainstream infrastructure for industries.
The future of blockchain isn’t about replacing traditional systems; it’s about enhancing them with transparency, trust, and automation. Companies that adopt blockchain early will be better positioned for innovation and long-term growth.
Explore How Flexlab Empowers Blockchain Solutions

Ready to elevate your business with innovative blockchain solutions? Flexlab enables organizations to design, develop, and deploy scalable blockchain systems that foster transparency, trust, and optimal performance. From private and public networks to consortium models, Flexlab delivers bespoke blockchain development services engineered to achieve your strategic goals.
Ready to Launch Your Blockchain Project?
📞 Book a FREE Consultation Call: +1 (416) 477-9616
📧 Email us: info@flexlab.io
Discover real-world success stories in our portfolio, explore our solutions, and start your blockchain journey. Contact us. See firsthand what our clients say about us and how we’ve transformed their blockchain vision into measurable success.
Keep expanding your knowledge by exploring the blog page for trending topics and expert insights, such as What is Web3? Why Web3 is the Future of the Digital Economy, What are NFTs and How Do They Work in Real Life, and A Step-by-Step Guide on Private Blockchain Development in 2025. Stay inspired and up to date by following Flexlab on LinkedIn for the latest innovations, success stories, and industry trends.”
Public vs Private Blockchain Insights: Finding the Perfect Business Fit
The Public vs Private Blockchain debate isn’t about which is better overall; it’s about what fits your business needs. Public blockchains bring transparency and global collaboration, while private blockchains offer privacy, control, and faster performance. Many organizations now prefer hybrid models, integrating both for greater trust and scalability. In today’s digital economy, blockchain is more than a trend; it’s a catalyst for growth, security, and innovation. Choosing the right blockchain today means staying ahead tomorrow. Businesses that implement blockchain early will gain a competitive edge, future-proof their operations, and open the door to new opportunities in the digital economy.
What is a private version of a public blockchain?
A private version of a public blockchain is a customized, permissioned network that uses the same foundational technology as a public blockchain but restricts participation to approved users. For instance, Quorum is a private version of Ethereum designed for enterprise applications. It maintains Ethereum’s smart contract functionality while providing enhanced privacy, scalability, and access control for business use.
What are the disadvantages of private blockchains?
Private blockchains, though efficient and secure for internal operations, have certain drawbacks. They can become overly centralized, which reduces the trustless nature of blockchain technology. Transparency is limited since only authorized members can view data. Because consensus mechanisms involve fewer participants, they may also offer lower security and resilience compared to public networks. These factors make private blockchains less suitable for open, decentralized ecosystems.
What is a consortium blockchain, and how is it different from public vs private blockchains?
A consortium blockchain is a semi-decentralized network governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity or the public. For example, Energy Web Foundation and IBM Food Trust use consortium models. It offers a balance between transparency and control, combining the efficiency of private blockchains with the shared governance of public ones.





















4 Responses